Post written by Alexa Leinaweaver, Live Animal Husbandry Coordinator
Happy World Wildlife Day!

Wildlife, while traditionally meaning all non-domesticated animals in an area, has expanded to mean all the fauna, flora, and other kinds of life. All species have evolved to be dependent on each other. Sustaining all kinds of life on our planet can only help the human race survive and prosper.
Some individual species are so vitally important to an individual ecosystem that they are considered to be a keystone species. So many other kinds of life depend on the keystone species that it would have a disproportionate effect if it should be removed from the ecosystem.
Colorado has amazing diversity in its wildlife. With the massive changes in altitude from the Rocky Mountains down to the Great Plains, the wildlife that live here have adapted to a wide range of micro-climates. With the variety of ecologies in the area, there are many keystone species that keep the whole system healthy. Some local examples include:
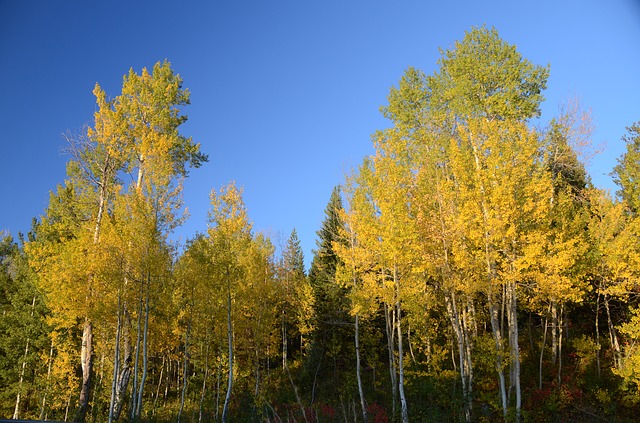

In the Mountains: Aspen trees
Quaking Aspen (Populus tremuloides) are, for many, a symbol of the Rocky Mountains. They cover 20% of Colorado’s forested land, or 5 million acres.
Aspen are a keystone species, supporting many birds, insects and mammals throughout the year and creating a highly biodiverse ecosystem. Because aspen love sunlight, groves are more open and bright than an evergreen forest. More variety of plant species can grow in the understory below an aspen grove. Additionally, as aspen are short-lived (70-150 years), they quickly add nutrients back into the soil around where they fall. Aspen propagate both with seeds and via cloning. A grove of clones can send up tens of thousands shoots per acre – which many grazing animals love to eat. Aspen shoots are actually higher in fat than many plant species, making it an especially important winter food source for deer and elk. The white bark of the aspen tree can also be used by many species as a food source in winter (elk, deer, beaver, rabbits, voles, mice, etc.), and year-round by a wide variety of insects. Several kinds of woodpecker, chickadees, nuthatches, kestrels, owls, and wood ducks will nest in the aspen.
Aspen trees are unfortunately in decline throughout the Rockies, up to a loss of 60-90% depending on the local climate. The primary cause is believed to be human behavior. Human efforts at fire suppression have allowed conifers to spread into aspen groves, shading the aspen and preventing them from thriving in the sunlight they love. Fire is also a natural part of the aspen’s life cycle: as the older above-ground aspen declines in health it should be cleared out by fire, prompting new sprouts. Without the fire, the sprouts are fewer and grazing animals have more impact on the grove. As the Aspen trees decline, hundreds of species will suffer.
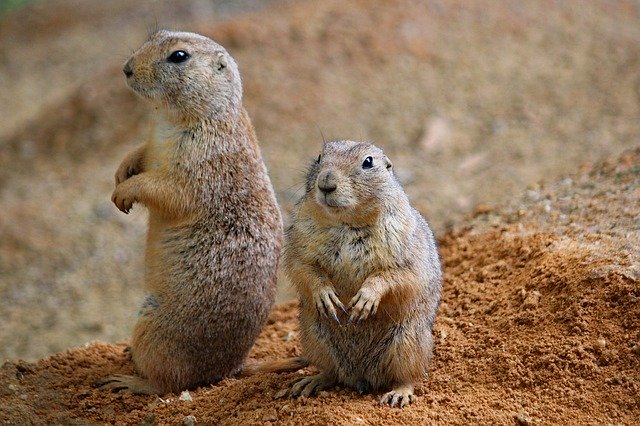

In the Prairie: Prairie Dogs
Prairie dogs (genus Cynomys) are a group of intelligent, burrowing rodents – actually a kind of ground squirrel – native to North American Grasslands. In Fort Collins area, you will see the Black-tailed Prairie Dog (Cynomys ludovicianus). Prairie dog colonies will dig a complex maze of burrows as their colony’s home for breeding, raising their young, and hiding from predators, maintaining the town over several generations.
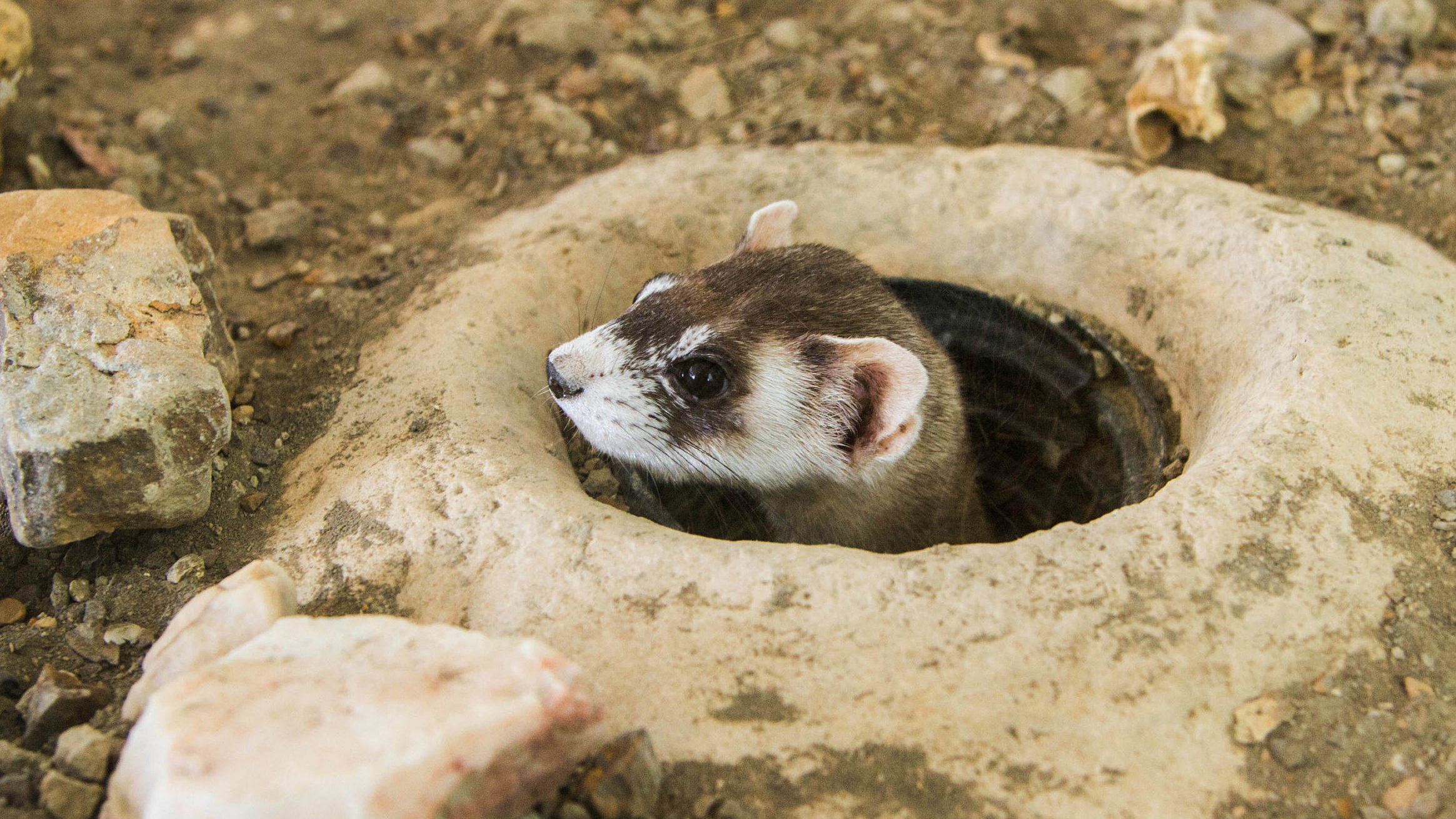
Prairie dog activities change the grassland ecosystem that they live in; they are often labeled “ecological engineers” for the way they shape the world around themselves. Burrowing will actually alter soil chemistry, as well as aerating the soil. Their grazing (both above and below ground) affects the plant life they live in, encouraging more diversity of plant species and plant productivity. The soil becomes richer in nitrogen and more fertile, supporting both more plants and a wider variety of insect life. Because of the positive effect prairie dogs have on the soil and the plant life above, grazing animals (including domestic cattle) often prefer to eat in the middle of prairie dog towns as the forage is better. Prairie dog burrows provide shelter and nesting habitat for many animals, including black-footed ferrets and burrowing owls. Prairie dogs are also a vital food source for a wide variety of predators: hawks, owls, ferrets, coyotes, badgers, bobcats, and rattlesnakes.
Prairie dogs numbers are vastly reduced from their historic populations. Many people believe that prairie dogs are pests, damaging crops or putting domestic animals at risk, and have actively persecuted the animals (e.g. target shooting, poisoning). Humans have also taken up most of what was originally prairie dog territory for agriculture and suburban sprawl. Between 1900 and 1960, 98.5% of prairie dog habitat was lost. Additionally, humans accidentally introduced the bacteria that caused the plague to spread, which can quickly wipe out entire colonies of prairie dogs. Even if you agree that they are pests, the loss of prairie dogs to our grassland ecosystems would have an enormous negative effect on hundreds of other species.
Celebrate World Wildlife Day
Celebrate World Wildlife Day this year by learning more about your local wildlife! Explore one of our many beautiful natural areas and observe the way that the wildlife interacts with each other. Or, visit the Fort Collins Museum of Discovery this weekend and see our Natural Areas Exhibit. Watch the Ferret Feeding Frenzy at 2:30 on Saturday or Sunday! This is not for the faint or squeamish of heart…
Continue Reading