Post written by Alex Ballou, Marketing & Design Assistant.
Time Travel: 1950s – 1980s
Have you ever wanted to travel back in time? In our latest blog we travel back to the historic decades of Fort Collins. We will start in 1910 and travel up to 1980. Join us as we scavenge the local history of our town.
1950s: Reformation
The need for reform in Fort Collins’ city government had been a local topic since the late 1940s. Voter reluctance to change the structure of the local government led city officials to move the city toward a more efficient system by using special powers, as with the placement of Guy Palmes as city manager in 1949. This movement necessitated a revision to the city charter. To this end the local chapter of the National League of Women Voters, formed in 1951, supported an analysis of the government, an updated charter, and voter education to convince the public. The effort was rewarded when, on October 5, 1954, a new city charter was adopted by special election.
Under the council-manager form of government, the City Manager was given administration of the city. He was hired and fired by the city council, attended council meetings, but had no vote. The mayor was chosen by the council, did not have the discretionary powers a mayor in the council-mayor form had, and authority for decision-making resided in the council.
In 1952 the local streetcar system became the last such operation in Colorado to end its services. The trolley had been costing the city money for several years and the cars were not in good condition. The establishment of an independent bus company in Fort Collins in June 1951 made the loss easier for local commuters. However, Bussard Bus Company’s Fort Collins operation did not match the trolley’s longevity. It ended its services in December, 1955.
1960s: Migration
The 1960s were turbulent years in Fort Collins. National unrest over the Vietnam War and the civil rights movement was reflected locally, especially on the Colorado State University campus. These crises combined with amazing growth in the city’s size and population, made the 1960s an unsettled period in Fort Collins history.
Rapidly increasing enrollment led to a building boom on the CSU campus. 7,304 students were enrolled at the University during the 1962-63 academic year. The figure grew to 15,361 in the 1968-69 year and plans were made to provide facilities for 25,000 students in the 1970s. Three new structures were built during the 1960s: Morgan Library, Moby Gym, and Hughes Stadium. In 1968, CSU became a member of the Western Athletic Conference and dedicated the new 30,000-seat Hughes Stadium to legendary coach Harry Hughes.
The social consciousness of the 1960s found expression through a variety of organizations and activities. One of these was the Peace Corps, which began with a feasibility study conducted at CSU in 1960. Maurice Albertson, an engineering professor who directed the University’s international programs office, was responsible for obtaining the grant for the study. By 1966, over 15,000 Peace Corps volunteer workers were scattered throughout the world.
1970s: Designing tomorrow
Campus unrest over civil rights issues and the Vietnam War continued at CSU in the 1970s. The alleged racist practices of Brigham Young University were a relatively volatile issue. While CSU’s administration refused to cancel a basketball game with BYU in January 1970, it did reluctantly allow a peaceful demonstration prior to the game. The demonstration proceeded as planned with no problems. However, during halftime, a group of predominantly black protesters rushed onto the floor of Moby Gym, fists held high in the “Black Power” salute. The protesters were slow to leave the floor and Fort Collins police were called on to clear the area. A student protest on a less serious matter occurred in April 1975. University administrators were reluctant to allow a Rolling Stones concert at Hughes Stadium that summer. The protest was relatively small, and the band was allowed to play. Traffic jams and discarded beer cans were the only adverse consequences.
The growth of Fort Collins between 1950 and 1970 completely changed the city. A new organization was founded in 1970 to help Fort Collins residents cope with rapid changes and to develop comprehensive long-range planning. Under Mayor Karl Carson’s initiative, a committee called “Planned Development for Quality” (PDQ), was formed. The name was later changed to “Designing Tomorrow Today” or “DT squared.”
“Design tomorrow today.”
In October 1970, DT reported projections up to the year 2000 concerning housing, transportation, education, employment, utilities, recreation, and social services. Task forces developed plans for public facilities and projects. On January 4, 1973, DT included: A new City Library; the Lincoln Community Center; Poudre River Parkway; land use planning and growth control; Transfort and Care-a-Van transportation systems; new parks; federally subsidized low income housing projects; sewer lines to Alta Vista and Andersonville; and restoration of the Avery House.
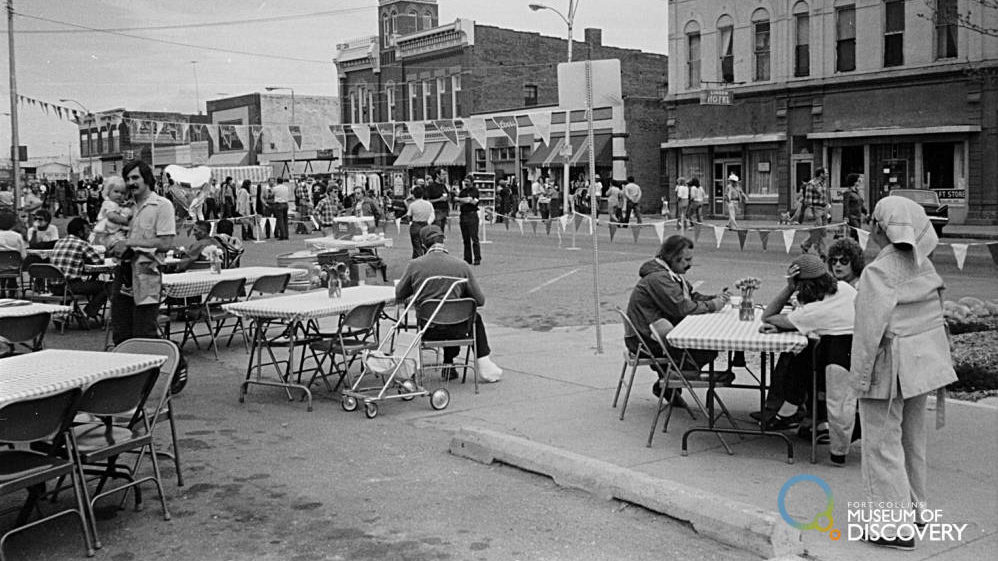
A popular park developed during the 1970s was the Lee Martinez Park, bordering the south bank of the Poudre River, west of the College Avenue bridge. The park was named after Librado “Lee” Martinez, a Fort Collins resident from 1906 until his death in 1970. Martinez was very active in community affairs. Shopping malls appeared in Fort Collins in the 1970s. The malls changed the face of the city and ended the downtown area’s dominance retail business. The major malls built during the decade were Foothills Fashion Mall, University Mall, and The Square, all off South College Avenue.
1980s: Growth
City planning continued as a major concern of the city of Fort Collins in the 1980s. Unincorporated border areas were a special problem. These areas often developed in ways inconsistent with standards established by the City, which created problems when these areas were annexed. To obtain some control over this development and avoid inefficient urban sprawl, the cities of Fort Collins and Loveland, joined by Larimer County, instituted the Urban Growth Area Plan in 1980. This plan designated a growth area boundary to accommodate expected development, provided guidelines for development within the boundary, established zoning regulations for development in the growth area, and contained an agreement which assured that land would be annexed by the appropriate adjacent city.
The development and restoration of downtown Fort Collins, a consideration begun in the 1970s, continued in the 1980s. In March 1981, voters created the Downtown Development Authority (DDA), made up of downtown property owners. Its board included one city council member. Their initial concerns were for parking and the undergrounding of utilities. The DDA supported projects with money from a five-mill tax levy in the DDA district and from tax revenue generated by new development. Projects the DDA has completed or supported included the parking garage on Mountain Avenue near Old Town and Old Town Square on Linden. Mitchell and Company of Denver revealed plans in 1981 for turning Old Town into a viable business district. 200,000 square feet of business space was included in the project, which sought to preserve historic buildings and build new structures compatible with them.
Increased growth was blamed, in part, for a two-thirds increase in felony crimes in Fort Collins between 1978 and 1981. One crime in Fort Collins that received worldwide attention in 1981 was the conviction of Eugene A. Tafoya for third-degree assault and conspiracy to commit third-degree assault. He had been charged with first-degree attempted murder and conspiracy. Investigators suspected that Tafoya had been hired by a former CIA agent to kill Faisal A. Zagallai, a Libyan dissident who had been critical of Mohammar Khadafy. However, there was not enough evidence to connect Tafoya with the agent.
To discover more about the decades and history of Fort Collins check out Fort Collins History Connection, the online collaboration between FCMoD and the Poudre River Public Library District: history.fcgov.com.
Continue Reading