Post written by Heidi Fuhrman, Discovery Camp Coordinator.
Daily Discovery: Water Week – Clean It Up!
Water is important to life on Earth but how can we make it safe to use and can we re-use it? Learn about the importance of water and take on a challenge to create your own filtration system and clean up some polluted water!
Supplies:
- Water
- Plastic bottle, milk jug, or other clear container
- Assortment of “filtration” materials:
- Napkins
- Paper towels
- Coffee filters
- Cotton balls
- Clay
- Sand
- Gravel/small pebbles
- Assortment of “pollution” materials:
- Dirt
- Small objects like paperclips
- Food scraps like peels
- Pieces of leaves/grass
- Food coloring
- Oil
- Salt/other spices
- Tape or rubber bands
- Scissors
Importance of Water
How have you used water today? Stop and think about it! Make a list!
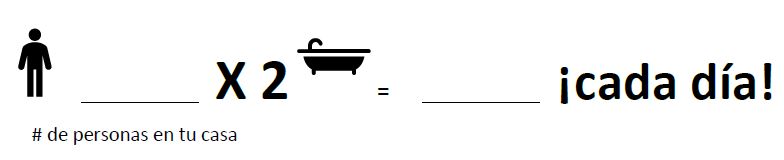
You probably thought of things like drinking or cooking or taking a shower, but did you think about things like brushing your teeth? Going swimming? Watering your yard? Giving your pets a drink? Flushing the toilet? Water is very important to our life on earth, we need it to survive! In fact, you can survive several weeks without food but only a few days without water! And we use a LOT of water each day. The average American uses 80-100 gallons of water each day. . .that’s 2-3 bathtubs full for just one person! How many people live in your house? How many bathtubs full of water are you using each day?

We use a lot of water each day, but there isn’t a lot of usable water in the world. Even though our planet is covered with water (over 70% of Earth is water!) only about 3% of the water on Earth is not salt water. . . and only about 1% of that 3% freshwater is usable (not locked up in glaciers, ice, the soil, or too polluted)! We have just a tiny amount of water to share with this whole globe, and as population and pollution increase that amount gets smaller and smaller! In dry or arid places (like here in Colorado and other parts of the American West) water is even more valuable!
Since water is so valuable it’s important to use every last drop! But water that flows in our rivers and streams isn’t usable for drinking, cooking, and cleaning right away. . .it contains pollutants and microorganisms that are harmful to humans. Is there a way to clean this water so it is safe to drink and use? We also waste a lot of
water down our sinks, drains, and toilets. . . is there a way to clean and re-use this water too?
There sure is a way to clean and re-use our water! Filtration is one of the best ways to start cleaning up our water so it’s safe to use. Filtration is the process of removing particles and pollutants from a liquid, and it’s how we start cleaning up our water (we also use safe chemicals and other to kill microorganisms an make the water potable which means “safe to drink”). While anyone can build a simple filtration system, Civil Engineers1 help design and build water treatment plants for our cities to help filter our water and make it safe for us to use. Today in our engineering challenge see if you can come up with a filtration system that can filter your polluted water! (Check out the worksheet at the end to help guide you!)
Note: The filtration methods used in this activity are a simple demonstration and the water should not be considered safe for drinking.
Engineering Challenge: Design A Water Filtration System!
Start by thinking about some sources of water pollution. If you turned on your faucet and no water came out, where would you find water near your house to use? What do those places look like? What could be polluting that water? Would you be okay drinking it?
Instructions:
- Thinking about the things that can pollute our water, mix up some polluted water of your own! Fill a jar or cup with some water and add pollutants! You could use bits of grass and leaves, dirt, oil, spices, small objects like paperclips, and food coloring. Ew! Gross!
- Gather your filtration supplies. You can use a variety of items, but we suggest a combination of napkins, coffee filters, paper towels, cotton balls, clay, sand, and gravel.
- Create your filtration system base. Cut the top off a plastic bottle, jug, or carton several inches below the top. A 2 liter soda bottle works best, but you can use a water bottle, juice jug, or even the top of a milk jug or carton. Place the top of your bottle inside the bottom or suspend over a pitcher or jar. Secure the two together with tape.
- Now we’re ready to start thinking like an Engineer and designing our filtration system! We’re going to use the Engineering Design Process to help us reach a solution today! (see steps on left). First, let’s think about what is the problem that we’re trying to solve? (Our water is polluted, and we need it clean!) Look at that polluted water you made:
• What types of pollutants do we need to filter out?
• Which of the filtration materials we have could help filter them out?
• What are some possible solutions to our problem? How could you design your filtration system?
Next, draw your idea for your design.
- Build your filtration system! Using the materials create layers in the top half of your filtration system base. At the end you’ll be pouring your polluted water into the top and watching it go through your filters to drip into the bottom. You want the water in the end to be as clean as possible! Think about:
• Which materials can filter which size pollutants?
• How can you order the layers to work the best?
• Predict which layer will filter which pollutants.
- Once you’re done designing it’s time to test your filtration systems! Give your polluted water a mix and then pour it in the top! Watch the water move through your filtration
system. Observe what the water looks like at the end.
• Does the water look cleaner?
• Are there any pollutants you weren’t able to filter out?
• Are there pollutants you can’t see but are probably still there (e.g. oil)?
• How could you remove the pollutants that you can’t see or couldn’t filter?
• How would you feel about drinking this water? Do you think you’d get sick? What about microscopic pollutants and organisms?
NOTE: The filtration methods used in this activity are simple demonstration and the water should not be considered safe for drinking.
- Take apart your filter and look at each of the different layers. Can you tell what each material filtered out? Did any of the materials surprise you by doing a better (or worse) job than you expected?
Level Up:
- Real engineers learn from their tests and try again to create an even better system! Empty the bottle, throw out your old filter materials, wipe out the bottle and try again! See if you can make the water even cleaner!
- Challenge someone! Make a big batch of polluted water and see who can filter it best!
Traducido por Károl de Rueda y Laura Vilaret-Tuma.
Descubrimiento en casa: Semana del agua – ¡Fíltrala!
El agua es básica para sostener la vida, pero ¿cómo podemos hacerla más segura para nuestro uso? ¿Es posible reutilizarla? Aprende más sobre su importancia y además ¡crea tu propio prototipo de un sistema de filtración para purificar agua contaminada!
Artículos necesarios:
- Un vaso con agua
- Botella, galón de leche o cualquier otro recipiente transparente de plástico
- Cinta adhesiva o bandas elásticas (ligas)
- Tijeras
- Variedad de materiales para filtrar el agua:
- Servilletas
- Toallas de papel
- Filtros para café
- Bolitas de algodón
- Arcilla/barro
- Arena
- Grava o piedritas
- Variedad de materiales para “contaminar el agua”:
- Tierra
- Objetos pequeños como clips para papeles
- Desechos de comida como cáscaras
- Hojas o hierba
- Colorante vegetal
- Aceite
- Sal/otras especias
La importancia del agua
¿En qué formas has usado el agua durante el día de hoy? Haz una lista.
Probablemente escribiste algunas maneras típicas de usarla, como para bañarte o para tomarla. Pero también usamos el agua en maneras menos obvias, como por ejemplo, para lavarte los dientes, al nadar, al regar las plantas, al darles agua a tus mascotas, ¡y hasta descargando el inodoro! Este elemento es muy importante para nuestro planeta, y definitivamente la necesitamos para poder sobrevivir. Es cierto que los humanos podríamos subsistir muchas semanas sin comida, ¡pero solamente unos días sin agua! ¿Y cuánta usamos generalmente? La persona promedio en Estados Unidos usa aproximadamente 80-100 galones de agua ¡en un solo día! Lo que equivale a 2-3 bañeras o tinas llenas de agua por persona. ¿Cuántas personas viven en tu casa? ¿Cuántas bañeras de agua están usando cada día? ¡Vamos a averiguar!
Usamos bastante agua todos los días, pero ¿puedes creer que en el mundo hay muchas fuentes de agua que no se pueden utilizar? Aunque nuestro planeta está cubierto con agua (más del 70% de la Tierra está compuesto de ella) solamente 3% es agua dulce. . . y solo 1% es utilizable (o sea, no es salada, no está en glaciares, congelada, en la tierra, o contaminada), así que tenemos un suministro finito de agua para compartir con el globo entero. Mientras la población y la polución ascienden, la cantidad de agua disminuye. En lugares secos o áridos (como aquí en Colorado) ¡el agua es todavía más valiosa!
Como el agua es un recurso tan precioso, es importante aprovecharla bien. Cuando este elemento fluye en ríos y arroyos no se puede usar inmediatamente para tomar, cocinar o limpiar, porque contiene contaminantes y microbios que son dañinos para los humanos. ¿Conoces alguna manera de purificarla y hacerla segura para su consumo? Además, también gastamos mucha agua potable a través del fregadero, en los drenajes y en el inodoro. . . ¿Habrá alguna manera para purificar y reutilizar esta agua?
¡Afortunadamente, la respuesta es sí! La filtración es una de las mejores maneras para limpiar nuestra agua y hacerla segura para su uso, ya que es el proceso utilizado para remover partículas y contaminantes de un líquido, siendo este el paso básico para empezar a purificar el agua (también se usan químicos seguros para eliminar microorganismos, lo que hace que el agua sea potable, o segura para consumir.)
Mientras que cualquier persona puede construir un sistema de filtración básica, los ingenieros civiles diseñan y construyen plantas purificadoras de agua para nuestras ciudades.
El reto de esta actividad incluye el que te conviertas en un ingeniero al diseñar tu propio prototipo de sistema de filtración para purificar el agua de tu casa. (Puedes utilizar la guía de abajo para facilitar esta actividad).
Aviso: Los métodos de filtración usados en esta actividad son únicamente para propósitos de demonstración y el agua resultante no debería ser considerada segura para consumir.
Reto de ingeniería: Diseña un filtro purificador de agua
Inicia pensando en las diferentes maneras en que se contamina el agua. Si no hubiera agua en tu casa, ¿a dónde irías para encontrarla? ¿Cómo sería ese lugar? ¿Aceptarías tomarla?
Instrucciones:
- Vamos a hacer nuestra propia “agua contaminada.” A tu vaso con agua, agrégale unos “contaminantes.” Puedes usar hierba, hojas, tierra, aceite, especias, objetos pequeños, colorante para alimentos, etc. ¡Ahora sí quedó muy sucia!
- Reúne los artículos que vas a usar para filtrar tu agua contaminada. Puedes utilizar una variedad de cosas, pero sugerimos una combinación de servilletas, filtros para café, toallas de papel, bolitas de algodón, arcilla, arena, o piedritas.
- Crea la base para tu sistema de filtración. Usando las tijeras, corta 10-15 centímetros de la parte superior de algún recipiente transparente. Una botella de 2 litros sirve mejor, pero también podrías usar cualquier otra o hasta un galón de leche. Pon la parte cortada de tu botella bocabajo dentro de la otra parte, y pégalas con cinta adhesiva o únelas con una liga.
- ¡Estamos listos para pensar como un ingeniero y diseñar nuestro propio sistema de filtración! Vamos a usar el proceso del diseño de ingeniería (el gráfico a tu izquierda) para
llegar a una solución. ¿Cuál es el problema que estamos tratando de resolver? El que nuestra agua está contaminada y necesitamos purificarla. Pensando en el agua contaminada que creaste, pregúntate lo siguiente:
• ¿Cuáles contaminantes tenemos que filtrar?
• ¿Cuáles de los materiales de filtración que tienes disponibles crees que puedan ser más eficientes para purificar el agua?
• ¿Cuáles son algunas soluciones posibles, y cómo podrías diseñar tu sistema para mejor resolver el problema?
Después, dibuja tu diseño.
- Construye tu propio prototipo de sistema de filtración. Pon los materiales (descritos en el paso #2) en forma de capas dentro de la base. Luego vierte el agua por encima de ellas y observa cómo se van filtrando los contaminantes. ¡El agua filtrada debe de aparecer lo más clara posible!
• ¿Qué materiales pueden filtrar eficientemente contaminantes según su tamaño?
• ¿En qué orden podrías reorganizar los materiales para que filtren mejor?
• Predice las capas que podrían filtrar a ciertos contaminantes.
- Después de fabricar tu filtro purificador, ¡es hora de ponerlo a prueba! Mezcla tu agua contaminada otra vez para incorporar todos los ingredientes y viértela por encima de tu sistema. Observa al agua pasando a través de las capas y también al agua que sale al fondo.
• ¿El agua filtrada parece más limpia?
• ¿Hay algún contaminante que no se pudo filtrar?
• ¿Crees que todavía hay contaminantes en el agua filtrada que no se pueden ver a simple vista, como por ejemplo, el aceite?
• ¿Cómo podrías eliminar los contaminantes que todavía existen o no se ven en el agua filtrada?
• ¿Cómo te sentirías si tuvieras que tomar esta agua? ¿Crees que te enfermarías?
¿Crees que quedan contaminantes y microbios microscópicos?
Aviso: Recuerda que los métodos de filtración usados en esta actividad son únicamente para propósitos de demonstración y el agua resultante no debería ser considerada segura para consumir.
- Empieza a desarmar tu filtro y observa cada una de las capas. ¿Puedes decir cuál de ellas filtró cada material? ¿Cuál funcionó mejor (o peor) de lo que esperabas?
Al siguiente nivel:
- ¿Sabías que los ingenieros verdaderamente utilizan este tipo de pruebas mientras continúan investigando para mejorar los sistemas que están diseñando? Ahora, vacía tus recipientes, límpialos bien, ¡y prueba otra vez! ¿Puedes lograr que el agua sea aún más limpia?
- ¡Convierte este experimento en un juego divertido y educativo para todos! Reta a tus familiares para averiguar quién puede crear el prototipo de filtración más eficiente. Y ahora que ya sabes más sobre el agua, ¡a seguirla cuidado!
¿Te gustaría descargar esta actividad? Haz clic aquí para obtener un archivo PDF.
Para encontrar actividades, ideas y mucho más descubrimiento en casa, ¡síguenos!
Continue Reading