Post written by Hannah Curtis, Education Assistant.
Fossils, Fossils Everywhere!
When you hear the word fossil, what is the first thing that comes to mind? Was it dinosaurs? If it was, great! Dinosaurs have and continue to play a role in planet earth’s history. We learn about them from a young age, and I know a few three year old’s that know more about dinosaurs than I do! It is a topic of inquiry, research and storytelling. Dinosaur fossils are discovered by paleontologists every year across the globe, especially Colorado (check out the latest discovery by DMNS), but dino fossils aren’t the only thing you can find close to home! Today I will bring you closer to mammal, and reptilian species that lived after the dinosaurs reign, during the Eocene epoch about 56 million years ago!
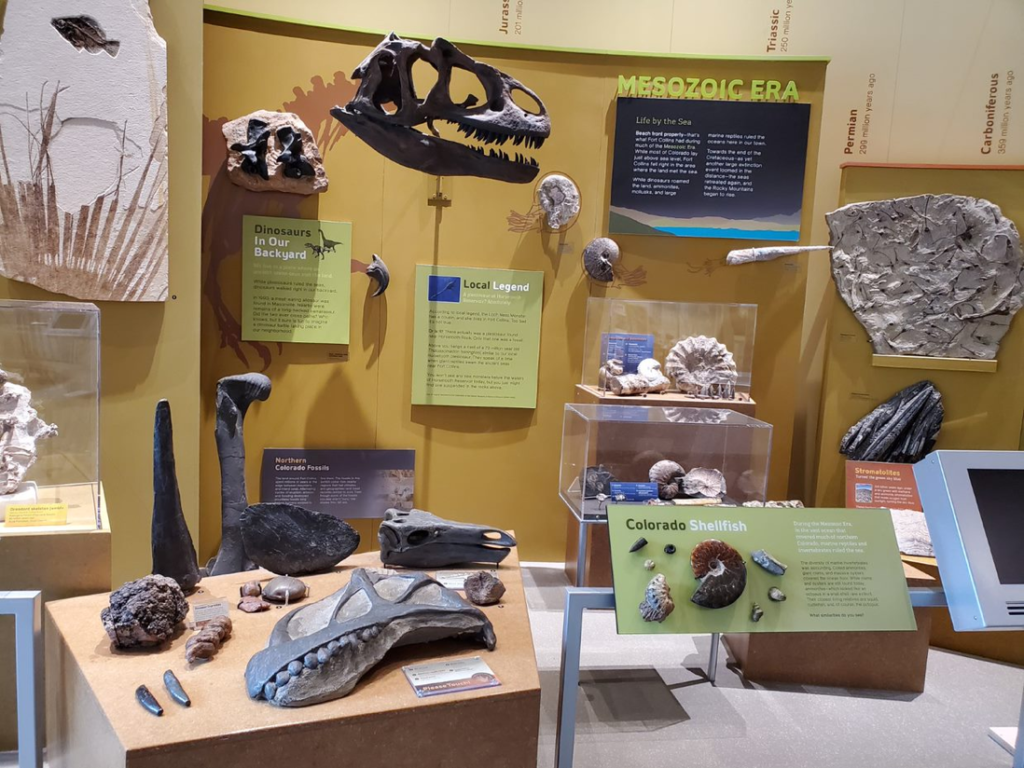
The Fossil Wall in the Wildlands & Wildlife Exhibit at FCMoD
For reference, here is the earth’s geologic timescale, beginning when the Earth was formed 4.6 billion years ago to the Holocene epoch of today. Dinosaurs lived throughout the Mesozoic epoch starting at 251 million years ago, while the Eocene epoch begins at 55 million years ago. Between those two time periods, the K-T extinction event occurred which eliminated roughly 80% of all species on the earth and began the Cenozoic Era. It’s hard to think of time as billions of years, so for perspective use your body to represent this geologic scale, now look at your pinky finger. This finger represents the Holocene epoch while the Cenozoic Era would be your arm. The modern human culture timeframe compared to the Earth’s life span is pretty small, yet not insignificant.
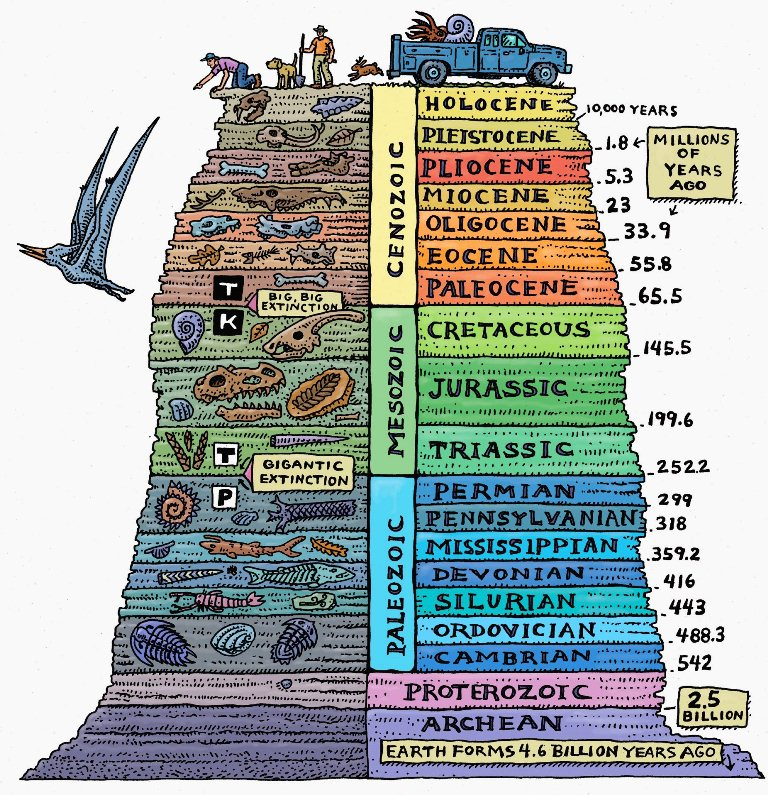
Geologic Time Scale
While studying at CSU to get my degree in Biological Anthropology, I was fortunate to participate in the departments Paleontology Field School season in Greybull, Wyoming! We spent two weeks in the hot sun, fossil hunting for tiny early primate jaws (smaller than a fingernail), to the teeth of large hippopotamus looking Coryphodon and everything in-between! Let’s start with the basics by talking about the different types of fossils that result from fossilization. For a quick overview of fossilization check out this video!

Coryphodon Recreation; American Museum of Natural History
Types of Fossils
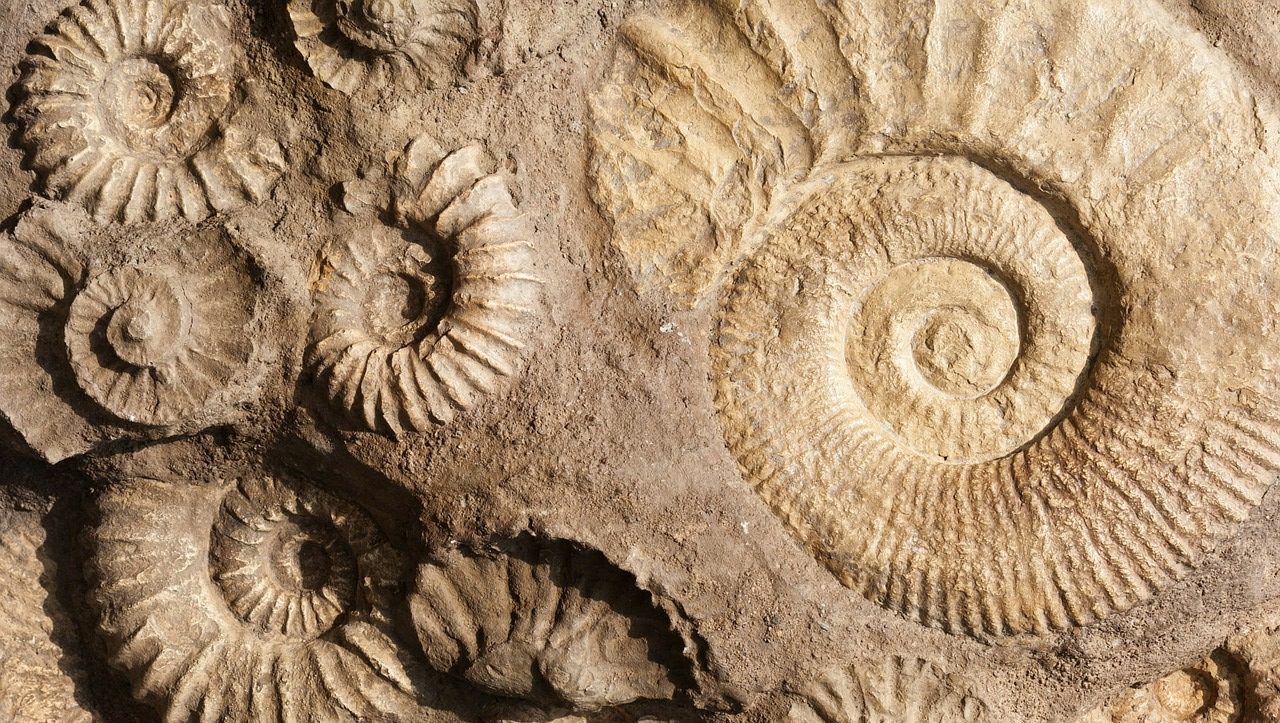
Body fossils are the fossils you might be most familiar with. These are most often bones or teeth that have been mineralized or petrified. Another example of a body fossil is turtle carapace or bivalve shells. Trace fossils occur when an object’s shape or pattern design is imprinted into the earth leaving a trace of what it was. The actual object is not fossilized, but instead leaves behind clues. Footprints or trackways are trace fossils along with the pattern and texture of crocodile skins.
One of my favorite types of fossils are coprolites which is fossilized animal dung. Burrow holes created by insects like the prehistoric wasp, are filled in with sediment and compacted to reveal fossilized burrows. Even after millions of years, fossils share bits and pieces of life, animal behavior and environmental aspects with paleontologists today!

Dinosaur Coprolite on display at FCMoD

Top left: insect burrow. Top Right: crocodile skin trace fossil. Bottom: fossilized turtle carapace
Fossil Hunting
Methods of paleontology will vary depending on the site or location as well as what era or time period you are looking at. Fossils coming from the Eocene generally aren’t going to be large femurs or skulls like dinosaur paleontology. Mammals and reptiles during this time weren’t even close the size of most dinosaurs so our methods didn’t including major digging or excavating. Our main method is surface prospecting. Seen in image 1 below, teeth and bones can actually be easily spotted on the grounds surface. The sediment is clay like, but easily eroded by rainfall and flooding. As erosion occurs, fossils rise the surface. Fossilized teeth shine and sparkle with bright sun making them easy to recognize. To speed up the process of erosion we use hammers and picks to break up and loosen the sediment. After a years worth of rainfall, a new layer will be revealed for the next years fields school students.
You won’t just find small bone fragments or teeth, at some sites or locals, full or partial skeletons have been found. These fossils will likely under multiple layers of sediment and require a delicate touch and will take more than one day to retrieve. Depending on the size of the fossil, you might have to cast the fossil. Using plastering materials, you can safely remove the fossil and surrounding sediment from the ground and transport it back to a lab to be prepared.
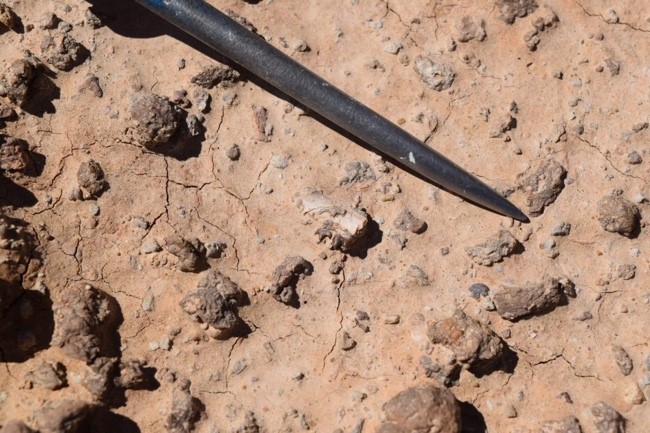

Fossil jaw and teeth

Students speeding up erosion process
Preparation and Curation
Paleontology doesn’t end in the field. Once you return to the lab with the fossils, they need to be properly curated and processed. Each fossil is given a field accession number and analyzed to identify the taxon of the animal, along with the elements of the fossil that easily identify it. This could be which teeth, or bone it is and if it was from the right or left side of the body. The fossil is also labeled by which local it was found in, who found the fossil, and for the geology nerds the paleosol stage! Accessing and curating each specimen provides valuable context for each fossil. Without it, the story of life, and evolution during this time can’t be properly pieced together. We found over 500 individual specimens during our field school year, and they all live in the CSU Paleontology Lab where research and preparation continue. Next time you hear the word fossil, will it still be dinosaurs you think of first?

Fossil Accessing Labels

Fossil collections storage