Post written by Alexa Leinaweaver, Live Animal Husbandry Coordinator.
National Bird Day: Winter Birds
Weather changes, snow is falling. But when you look out your window, there are still a bunch of birds hanging out. Which birds are here in the winter, and how do they survive?
Migration
Migration is a strategy that many animals use to cope with seasonal changes. Generally migration seems to be triggered by birds following their food supply or seeking a new type of food, as well as seeking more comfortable weather conditions.
We are most familiar with migration from an area closer to the poles in summer, and toward the equator in winter. This is known as Longitudinal Migration, as it is on a north-south axis. Migration distance can range from thousands of miles each way to only a short distance. While we mostly think of birds leaving Colorado for warmer weather, we get some migrants coming to stay here from much further north. Some examples of birds that migrate to the Fort Collins area for winter:
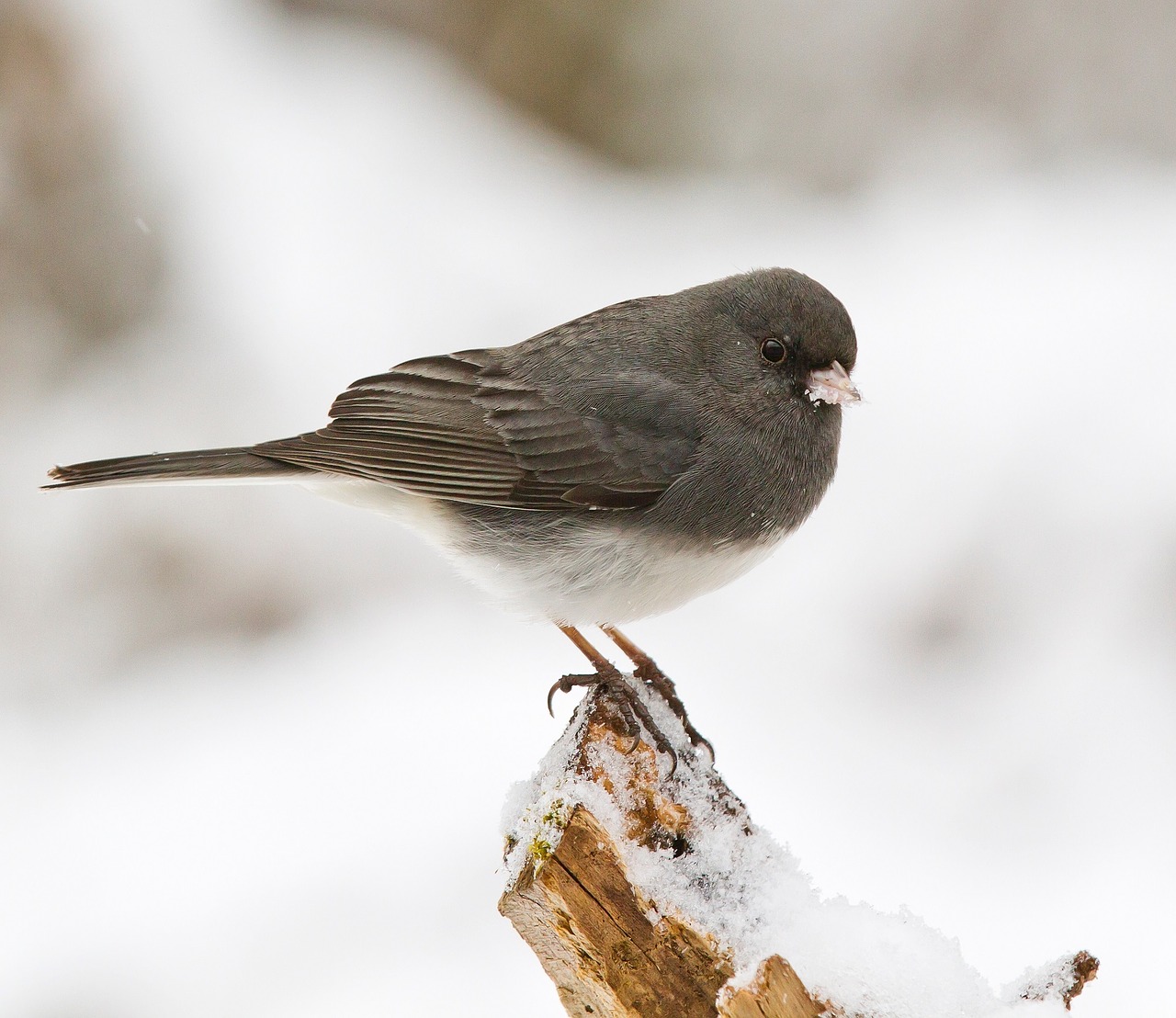
- The Dark-eyed Junco spends its summers breeding in Canada and Alaska, and moves down into the continental United States during winter. Juncos are easily recognized by their behavior, hopping around the ground seeking food, and the black and white flash of their tail when they take flight. They are colloquially known as “Snowbirds”.

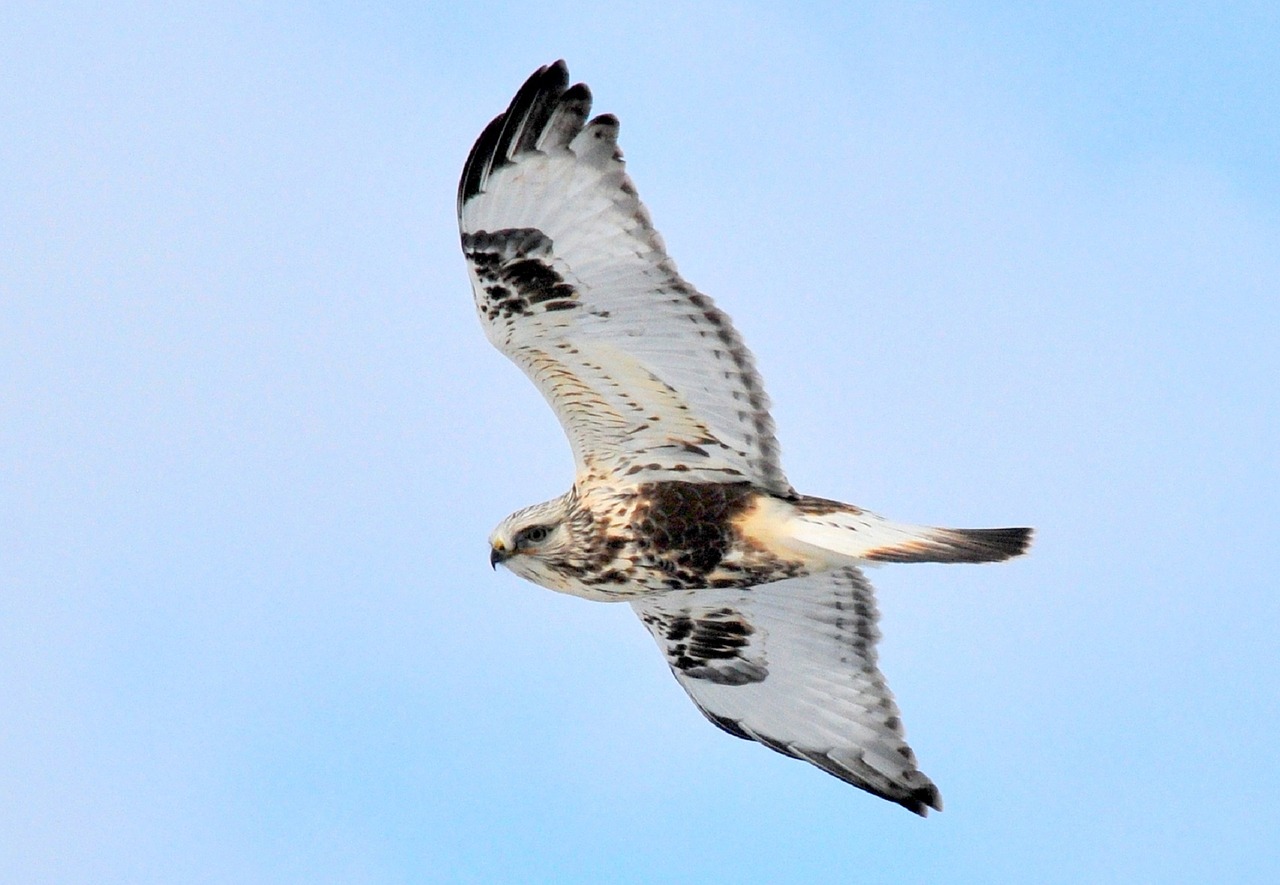
- The Rough-legged Hawk breeds in the Arctic, but winters in the U.S. and southern Canada. It gets its name from the fluffy feathers covering its legs – an excellent adaptation for a bird that spends its summers in the Arctic as well as for our snowy Colorado winters.

- Most Bald Eagles spend their summers further north in Canada and Alaska. They will migrate into Colorado in winter where they breed, usually January through March. (We do have some year-round resident bald eagles in the area as well.)
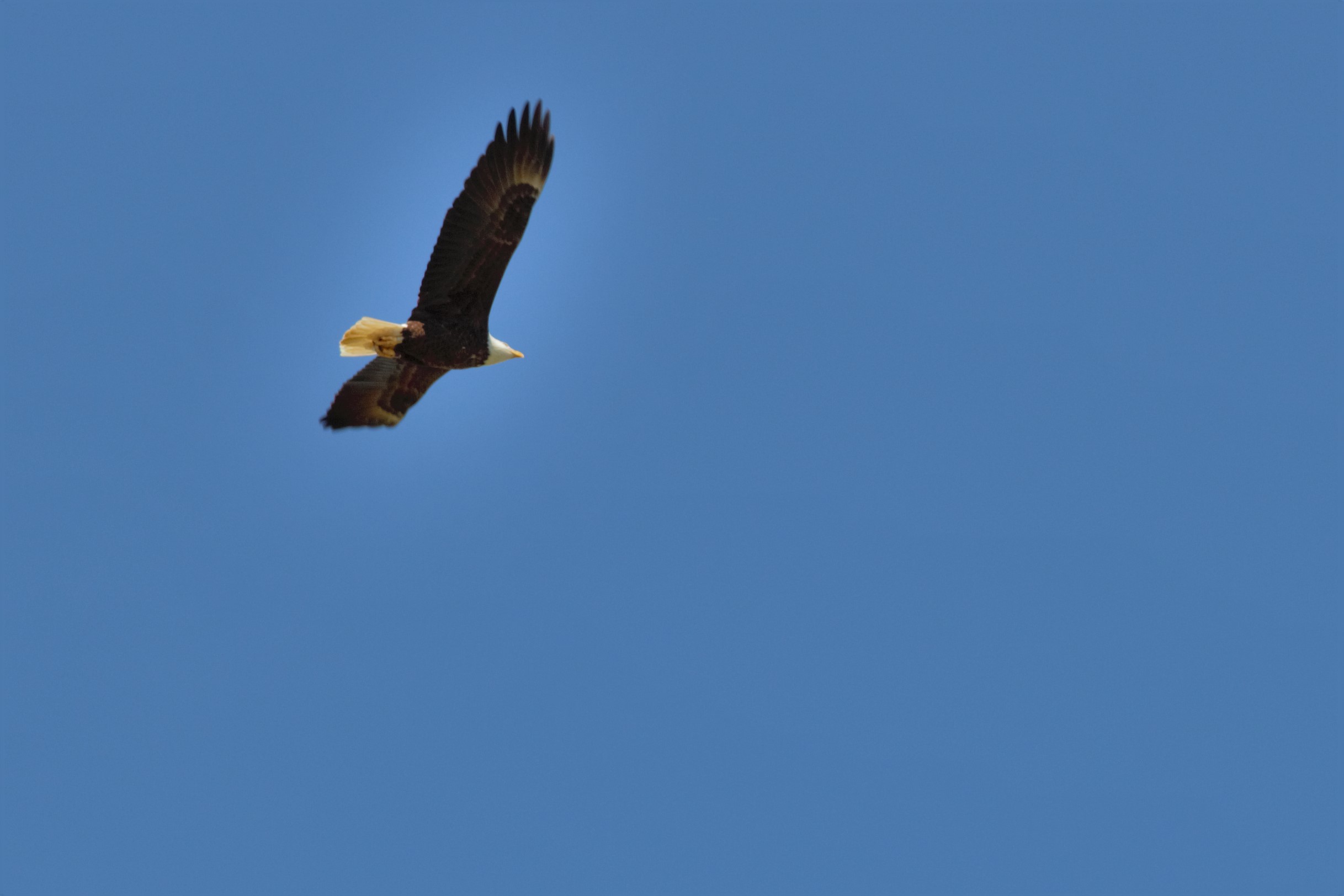

There are also birds that migrate a short distance, but for a big change in altitude: Altitudinal migrants. Most of the altitudinal migrants in the U.S. are in the American West, thanks to our Rocky Mountains. Many of us humans have experienced the dramatic difference in weather and temperature between the plains and up in the Rockies.
- Most Prairie Falcons winter in the Great Plains, hunting Horned Larks and Western Meadowlarks. In summer, they move up to 11,000 feet in search of abundant ground squirrels and pikas.
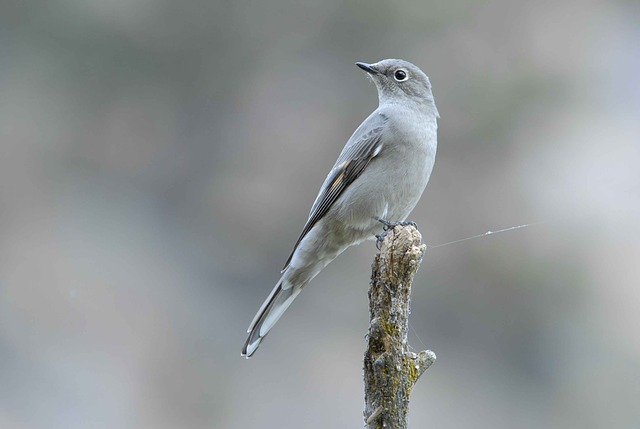
- The Townsend’s Solitaire spends its summers in the mountains, then moves to lower elevations in winter. They switch food sources from mostly insects in summer to fruit, mostly juniper berries, in winter. They can get extremely territorial over their chosen patch of juniper trees, defending them against solitaires and other bird species.

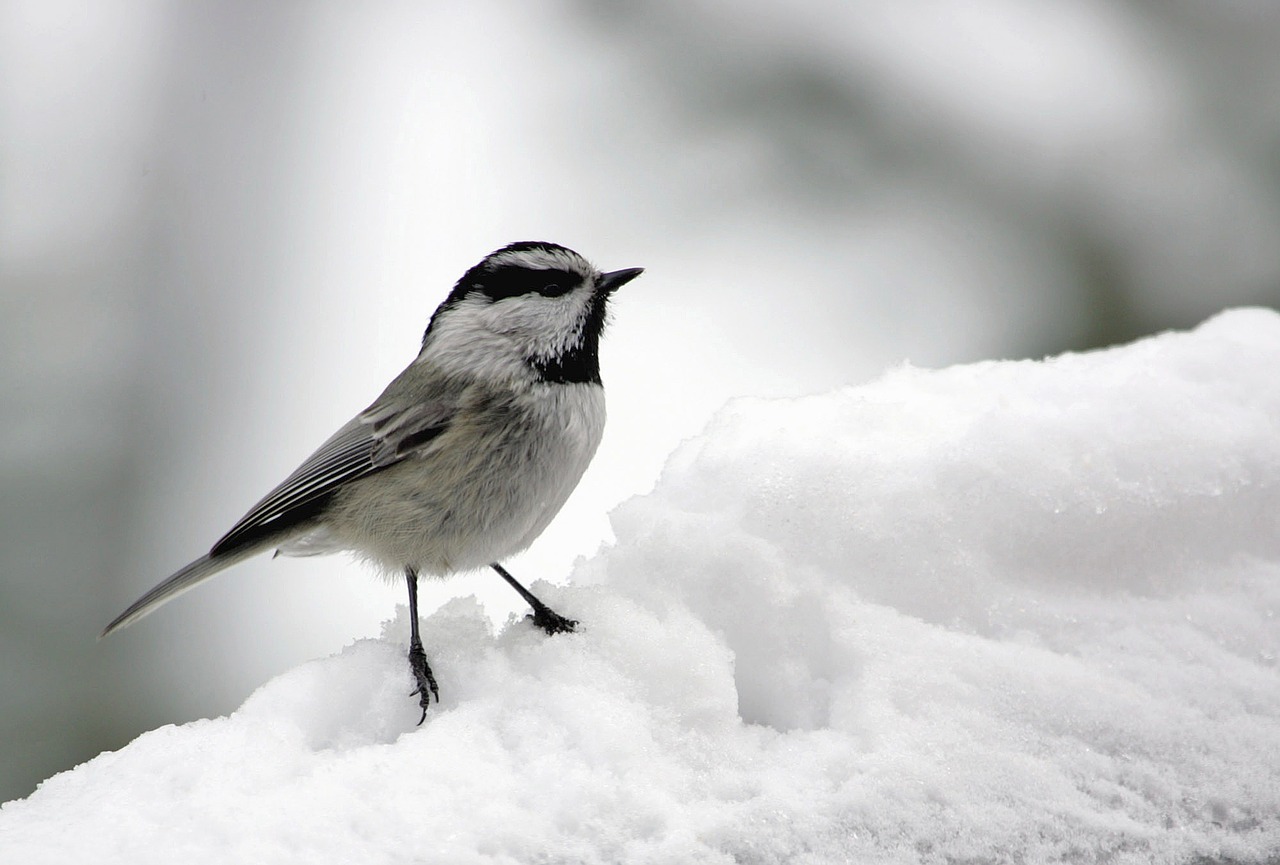
- Immature Mountain Chickadees are known to migrate to lower elevations. However, once they are old enough to select a breeding territory, they will generally stay there year-round. (It can be very challenging to distinguish them from our usual Black-capped Chickadees who stay in Fort Collins area year-round. Look for a white “eyebrow” on the Mountain chickadee that the Black-capped lacks.)

Other Adaptations for Winter Survival
For us humans, it seems logical to escape the cold and snow by going south for warmer weather. But birds have amazing adaptations to help them survive weather that we find daunting.
- Feathers are the best insulation we know of. Imagine curling up inside a cozy down overcoat – birds have one naturally! They can retain heat by fluffing out their feathers, trapping more air underneath to keep them warm. Birds like chickadees or wrens fluff up so much that they look twice as fat in winter! Many birds, like the American Goldfinch, will also change out their sleeker, brighter summer coat for a thicker, drabber winter one. They get better camouflage as well as better insulation.
- Some birds, like crows, will cluster together and share body warmth. Smart birds like crows and other corvids can also communicate about food sources and predators.
- Many birds will also plan for the winter by putting on fat. It acts both as insulation to keep warm and as an energy source if hunting for food doesn’t go so well.
- Birds are also good at predicting when the weather will turn bad and a blizzard is coming. They will eat extra food in advance of the storm, then hunker down and save calories for body heat while it snows.
- Several species will change what kind of food they eat. The Townsend’s Solitaire and Prairie Falcon, described above, are great examples. Some birds will also stash food in preparation for the cold – if you have a birdfeeder that gets extra busy in fall, some of your avian visitors are probably caching food for later.
Birding in Winter
Celebrate National Bird Day this year by spending some time outside, looking at our seasonal visitors! But remember, winter can be a difficult season for any wild animal. Keep your distance so they don’t waste their precious energy flying or running away from you when you get too close.
Photo courtesy of Alexa Leinaweaver.