Post written by Alexa Leinaweaver, Live Animal Husbandry Coordinator.
Happy Reptile Awareness Day!
What makes a reptile a reptile?
Reptiles are vertebrates with scaly, with dry, water-proof skin. They generally lay eggs with leathery shells, unlike the hard-shelled eggs of birds. Reptiles are poikilothermic, generally termed as “cold blooded,” which means they maintain their body temperature through external sources of heat such as basking in the sun. Reptiles that live in northern latitudes – such as those native to Colorado – will become dormant in winter: their bodily processes slow in the cold.
There are four orders of animal that make up the class Reptilia: Testudines (turtles), Squamata (lizards and snakes), Crocodylia (crocodiles and alligators), and Rhynchocephalia (tuataras). Turtles and crocodiles first appeared on earth along with the dinosaurs!
Reptiles live on all continents except Antarctica.
Meet FCMoD’s Reptiles:
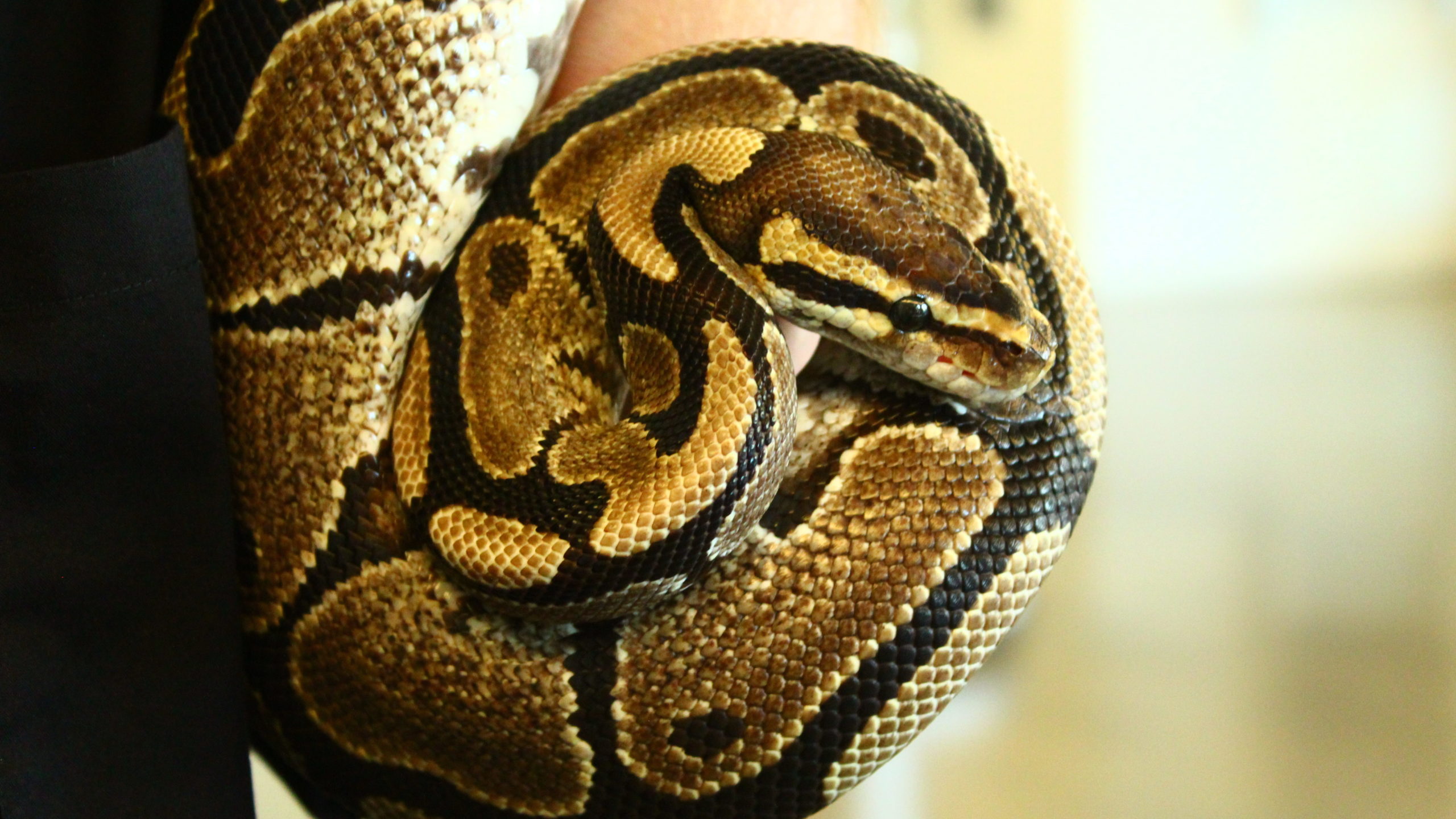
Ball Python (Python regius)

Our Ball Python, named Slinky, is approximately 20 years old. The oldest Ball Python on record lived to be 40 years! The species is native to sub-Saharan Africa. Ball Pythons often burrow underground to stay cool in the African heat. They also may cool themselves in pools of water.
This python is named “ball” because when threatened, it curls into a ball for protection, hiding its head and neck (the most vulnerable parts) in the middle of the ball. Ball Pythons are also called “Royal Pythons,” as there is a story that royalty in Africa would wear the snakes as jewelry, because the camouflage pattern on their scales is so beautiful.
Ornate Box Turtle (Terrapene ornate)

Our Ornate Box Turtle, Tara, is a species native to Colorado and the Great Plains. She eats fruit and vegetables – she loves pear the most! – and insects. Turtles don’t have teeth, but instead a sharp beak that they can use to crunch through an insect’s exoskeleton or bite into a tough root.
Turtles have a shell that protects them from predators, made from keratin (the same thing our fingernails and hair is made from!). It is attached inside to their spine and ribs. Tara and other turtles (though not tortoises) are able to pull their legs and head completely inside the shell when threatened.
In a cold Colorado winter, Ornate Box Turtles will dig a hole in the ground and hibernate to survive.
Leopard Geckos (Eublepharis macularius)

Our two Leopard Geckos are native to Iran, Afghanistan, Pakistan, and parts of northern India, where it is dry and rocky. It can get very hot there during the day, so they generally stay in the shade or in burrows while the sun is out. They are active at dawn and dusk when the temperature is more comfortable. As winter in that area can get quite cold, these geckos will stay underground the entire time and hibernate.
Leopard Geckos will hunt for insects, spiders and scorpions, as well as other lizards. A fascinating fact about them is that they are immune to scorpion stings! These reptiles keep their food reserve in their tails, which is why the tail looks so large compared with other lizards. When they are threatened by a predator, they can even drop their tail completely! The predator will be distracted by the tail while the gecko gets away. The tail eventually grows back.
Geckos use their tongues to clean their eyes. They will also use their tongues to figure out what is in the environment around them.
How you can celebrate Reptile Awareness Day!
- Take some time to learn about reptiles! There are some amazing species out there, and the more we know about them the better humans and reptiles can live together.
- Visit FCMoD and observe our reptiles in our Animal Encounters exhibit! Observing a reptile will help you understand and appreciate these amazing creatures.