Have you ever wondered how the music you listen to made it to a streaming platform, CD, or the radio? Sure you’re aware the song is recorded in a studio, but then what happens? How does it get to sounding how it does, ready for an album? And then how does it get released from there? This blog will inform you about the processes of music production, and how our favorite songs we hear start from an idea, to a tangible recording in our hands!
Writing the song
Each artist has a different process for writing songs. Many well-known bands and singers will often have a producer. Producers have a very important role in the process of getting songs ready to release. They often help the songwriting process by making suggestions of what the artist could add or take out of the song they’ve written so far, whether it be changing the chord progression, adding a bridge, suggesting words for lyrics that fit better, or anything to improve the song! It’s also important to note that not all artists write their own songs. Often in pop music, a songwriter writes songs for specific singers. Did you know that Rihanna’s “Umbrella” was originally written by a handful of producers for Britney Spears to sing? She turned it down as she just finished her album, so it was floated over a couple artists until Rihanna accepted it. Once a song is written, it’s ready for the studio. Sometimes artists even go into the studio without having finished writing. Sometimes it’s because the producer will be there to help write, or the creative atmosphere of the studio helps the artist to write!

Recording
The recording process also looks different from artist to artist, but accomplishes the same thing. Professional recording sessions take place in a studio, where the rooms are specifically arranged for high quality sound. Rooms can be built specifically to absorb and reflect certain frequencies, and/or have sound proofing gear installed. Sometimes artists take a DIY approach and record their entire album using gear in their bedroom! In a professional setting, recording engineers oversee the process- placing mics properly on the instruments, getting appropriate levels set, making sure everything is set up to sound the best it can. Producers also help artists find the sounds that will help get the song’s vision across, whether it’s a special technique for setting up a microphone to get vocals sounding a certain way, or setting guitar tone. Then, a song is usually recorded over and over, with enough takes to have every part of the song sounding good. In a multi-instrumental band, drums are often recorded first so that each other musician has a foundation to overdub their parts. Overdubbing means recording a track over an already-existed recording track, so in this case, the drums are already recorded, and everything else can now be overdubbed. Bass is typically recorded second, then guitar and remaining instruments. Vocals are almost always last. With the digital technology in recording nowadays, it’s very easy for musicians to fix a measure or note they may have messed up, in which they will punch in. Punching in means the engineer will start the recording at the part where the mistake is, and the musician can simply play correctly over the wrong part without having to redo the whole song. Artists that recorded before this technology was available had to redo the entire song if there was one big mistake! However, even with this technology now, recording is a lengthy process, and one album may take months or years.
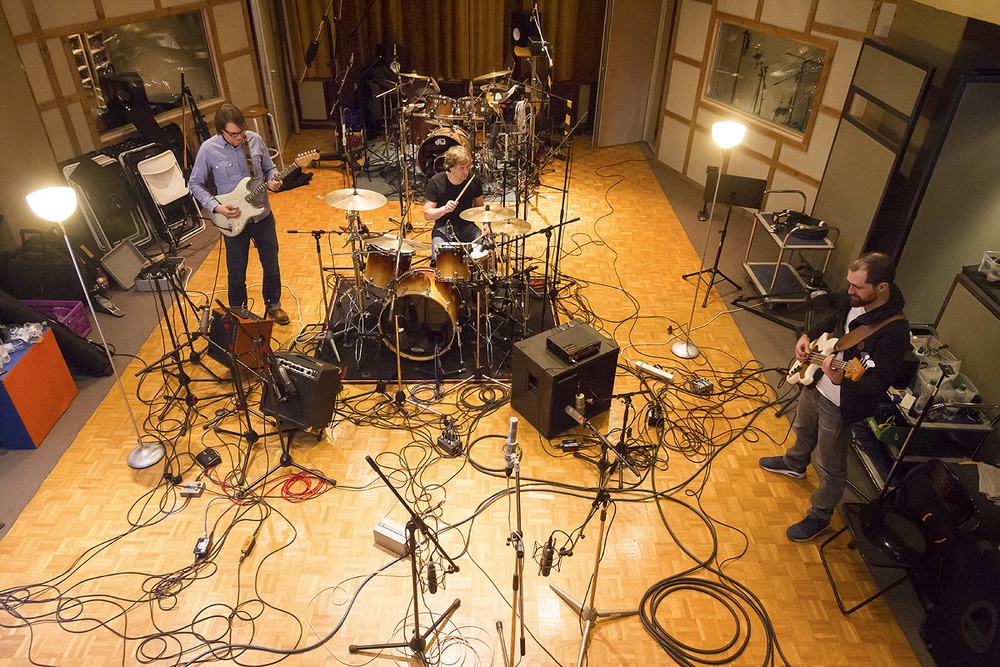
Mixing
After the recording is complete, it’s time for an engineer to mix the song. This means setting levels of each of the instruments, making sure they’re all well-balanced and heard in the song, as well as adding EQ and other things to make the song come to life. This process can take a couple days or weeks for one song, and months for an album. The artist communicates the vision they want for the song so the engineer can get the sounds dialed in and make it happen. The artist may want a warm, bright mix with punchy high frequencies for a pop tune or a darker mix with depth. The mixing process is just as creative as the songwriting process, the mix having the ability to transform the recording and give it a completely different feel. Often the engineer will send their mix to the artist, the artist will give feedback of what they want to sound different, the engineer makes a new mix, sends it over, and it happens all over again until the artist is satisfied.
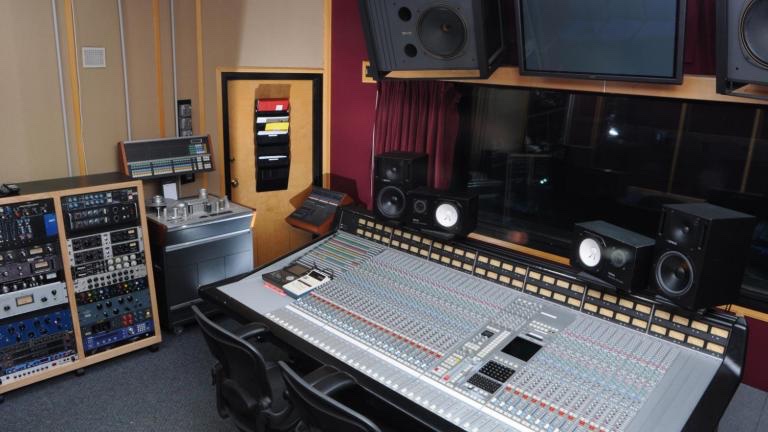

Mastering
Once the mix is complete, the song needs to be mastered. Mastering is the process of getting a track ready for distribution by balancing it to be at the level of volume and quality of songs that are already established. The mastering engineer starts by bringing the track up in volume to be as loud as songs already out there. They may download an existing song to use as a reference track to set the level of the song they’re working with. This way, after the song is released, its volume isn’t a lot quieter than all the other songs on your playlist. Then, the mastering engineer may widen the mix with stereo enhancement (balancing the left and right of the audio). After that, more EQ and compression may be done to polish off the song.

Distribution
Now the song is ready for consumption! Artists will then decide how they want to release their music- on CD’s? Spotify? Youtube? At this point, the completed song file is submitted to distributors to make CD’s, Vinyl, tapes, uploaded on streaming services, or sent to radio stations. Now it’s a tangible product for anyone to access and listen to! Can you imagine your favorite songs going through these processes? There’s so much time and work that goes into one song that takes 3 minutes to listen to. Does that change how you view what you listen to?






 The year 1949 was also monumental because Leo and coworker George Fullerton completed the first prototype for the famous Esquire guitar. The prototype (pictured to the left) shared a similar body shape with later guitars of the same vein. The shape was a dreadnaught style with a single cutaway, allowing easy access to the upper frets of the guitar. In the next year, 1950, the Fender Electric Instruments Company officially released the first mass produced guitar ever, the Fender Esquire. The biggest change from the prototype to the first model (seen below) was the headstock shape. The Esquire was a solid-body, single pickup electric guitar – a pickup is a magnet that “picks up” the vibration from the strings and sends it to an amp. The pickups on the first Esquires pictured are the metal boxes at the end of the strings. The guitar also had one knob to control the overall volume and one knob to control the tone, or timbre, of the guitar’s pickup. The first advertised color scheme was a black body with a white pick guard, but later produced Esquires had a blonde body with a black pick guitar (as pictured). This first model also did
The year 1949 was also monumental because Leo and coworker George Fullerton completed the first prototype for the famous Esquire guitar. The prototype (pictured to the left) shared a similar body shape with later guitars of the same vein. The shape was a dreadnaught style with a single cutaway, allowing easy access to the upper frets of the guitar. In the next year, 1950, the Fender Electric Instruments Company officially released the first mass produced guitar ever, the Fender Esquire. The biggest change from the prototype to the first model (seen below) was the headstock shape. The Esquire was a solid-body, single pickup electric guitar – a pickup is a magnet that “picks up” the vibration from the strings and sends it to an amp. The pickups on the first Esquires pictured are the metal boxes at the end of the strings. The guitar also had one knob to control the overall volume and one knob to control the tone, or timbre, of the guitar’s pickup. The first advertised color scheme was a black body with a white pick guard, but later produced Esquires had a blonde body with a black pick guitar (as pictured). This first model also did  not have a truss rod. A truss rod is a piece of metal that runs inside and along the neck. The end of the rod can be turned with a tool which will push or pull the neck in one direction or another. This is used to help straighten the neck when the tension from the strings causes it to bend over time. Only about 50 of these first Esquires were made. As orders increased, the needed improvements were recognized by Leo and George. Just months later they set out to revamp their already very popular electric guitar model.
not have a truss rod. A truss rod is a piece of metal that runs inside and along the neck. The end of the rod can be turned with a tool which will push or pull the neck in one direction or another. This is used to help straighten the neck when the tension from the strings causes it to bend over time. Only about 50 of these first Esquires were made. As orders increased, the needed improvements were recognized by Leo and George. Just months later they set out to revamp their already very popular electric guitar model.
 Leo did not stop there in 1951. That same year he released his company’s first electric bass model, known as the Precision Bass (a 1952 model to the left). This model is still mass produced today and is one of the most popular and used bass guitars. Next in line came Leo’s second guitar model, that would achieve him even more historic fame and forever make him an icon in the guitar world. The Fender Stratocaster followed the Telecaster in 1954, and took the world by storm. It has stood atop the pillar of modern guitar as the most recognized shape and symbol of the instrument. It has been used on countless famous recordings and is only second in Fender origin to the one and only Telecaster.
Leo did not stop there in 1951. That same year he released his company’s first electric bass model, known as the Precision Bass (a 1952 model to the left). This model is still mass produced today and is one of the most popular and used bass guitars. Next in line came Leo’s second guitar model, that would achieve him even more historic fame and forever make him an icon in the guitar world. The Fender Stratocaster followed the Telecaster in 1954, and took the world by storm. It has stood atop the pillar of modern guitar as the most recognized shape and symbol of the instrument. It has been used on countless famous recordings and is only second in Fender origin to the one and only Telecaster.

