Post written by Alex Ballou, Marketing & Design Assistant.
Time Travel: 1910s – 1940s
Have you ever wanted to travel back in time? In our latest blog we travel back to the historic decades of Fort Collins. We will start in 1910 and travel up to 1980. Join us as we scavenge the local history of our town.
1910s: Development
The 1910s were turbulent for Fort Collins, as for the rest of the world. The first world war dominated the news of the latter half of the decade. However, there were also many important civic developments. Among these was the city’s change to a commission form of government in 1913.
Also important to the town’s continued development was the sugar industry, which continued as the dominant economic force of the area. In September 1919, The Fort Collins Express noted that an estimated twenty million dollars had been paid for sugar beets in Larimer County in over a period of seventeen years.
College students built and whitewashed the “Aggie A” on a hillside west of town in 1912. Three years later the school and the town celebrated the football team’s first conference championship. The Fort Collins Express expected the title to bring more students and prestige to the school and consequently benefit the town. Annually, the “Aggie A” is still painted by college students.
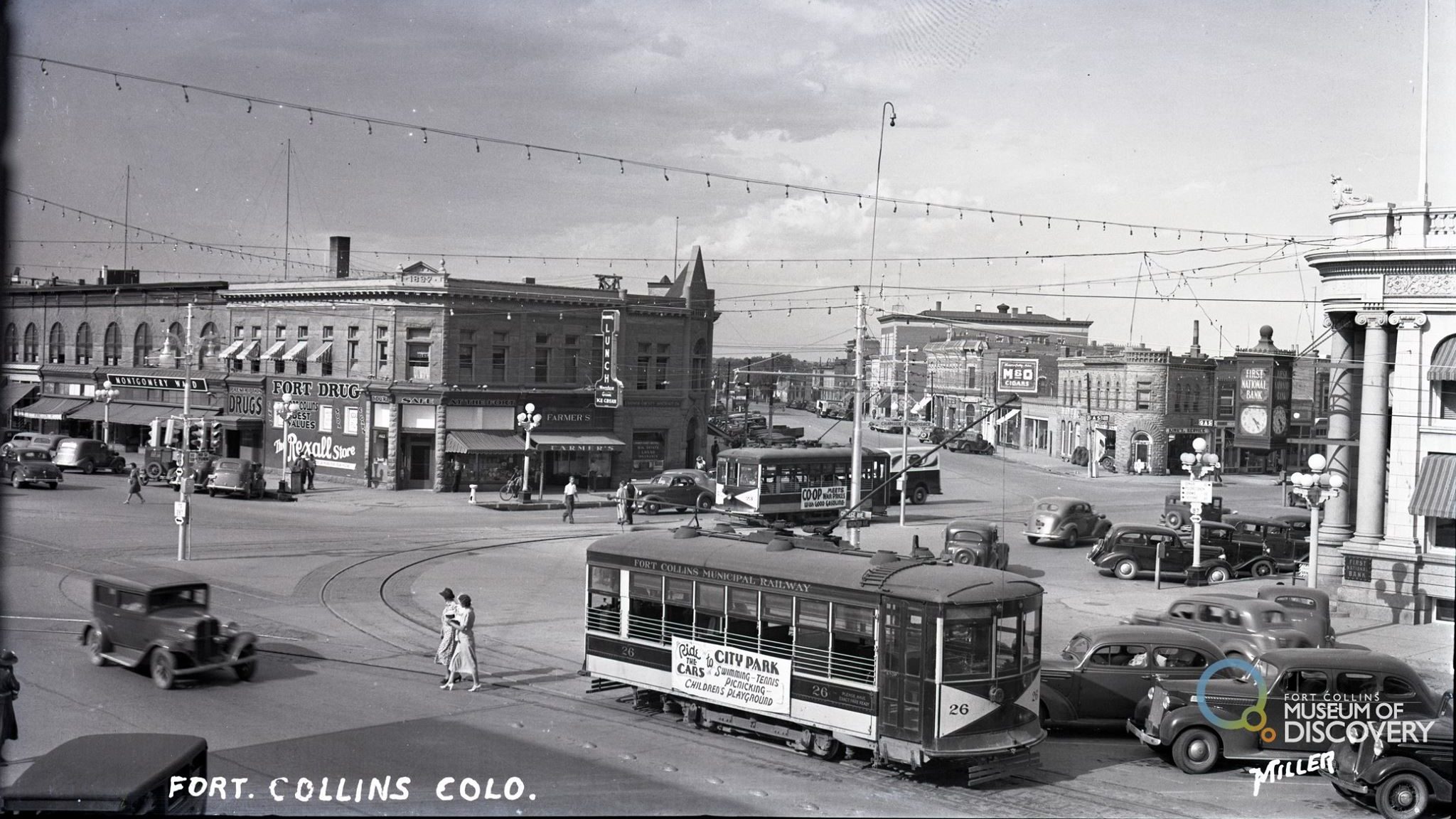
1920s: Prospering
Despite a generally depressed farm economy after World War I, Larimer County farmers were comparatively prosperous. The Fort Collins Express-Courier (the two local papers combined in 1920) claimed that no other county in Colorado fed as many sheep and cattle as did Larimer County.
Beet growers were also still doing well. An attractive contract in 1925 between Great Western Sugar Company and the Mountain States Beet Growers Marketing Association guaranteed eight dollars per ton plus incentive bonuses.
Larimer County was also prospering industrially. It ranked third among Colorado counties in manufacturing. Most of the factories were in or near Fort Collins. The biggest producers were the sugar factory and the Ideal Cement plant built in 1927 near La Porte.
“History is the whole series of past events.”
History contains the good, bad, and ugly – and the 1920s witnessed a resurgence of the Ku Klux Klan in Colorado. The Klan gained control of state politics during the early part of the decade and had many men in elective and appointive offices. Klansmen in Fort Collins could be found in courthouse offices and city hall. During one rally, sheet-covered KKK members marched from North College Avenue to Lincoln Park. However, the Klan did not place a significant number of its people into local public offices. Its influence faded during the latter half of the decade.
A political figure on the rise, Franklin D. Roosevelt, visited Fort Collins in 1920 on a campaign tour as a vice-presidential candidate, and spoke from the courthouse steps against increasing the Navy and for the League of Nations.
1930s: Depression
The Great Depression of the 1930s worsened an already dismal situation. A farm economy which had been depressed since the end of World War I sank even lower as prices fell to new lows for agricultural commodities. Drought during the first half of the decade, combined with a grasshopper plague, added to the hardships, especially for plains farmers, many of whose crops were lost.
In the Fort Collins area, the water shortage became so severe that the city banned the use of water from the waterworks system for lawns and gardens in September 1934. The Cache la Poudre River was said to be at the lowest level known since settlement of the valley. In March 1935, the city council approved a watering rule which allowed townspeople to water their lawns one day per week.
The Extension Service of Colorado Agricultural College played a vital role in providing relief to afflicted farmers. Extension personnel helped to gather and distribute food, protect crops from grasshoppers, and promoted tree cultivation. The Extension Service also participated in the development of several New Deal programs. The College’s Experiment Station also worked to alleviate the effects of the drought and grasshoppers and conducted other beneficial projects.
1940s: Defense
The war in Europe, which began in 1939, had almost immediate effects in Fort Collins.In October 1940, 3,881 Larimer County men registered for Selective Service. A national draft was held at the end of the month. Battery A, of the 168th Field Artillery and Medical Detachment, was inducted into the U. S. Army in February 1941.
Because of Colorado State College’s tradition of supplying military instruction, an R. O. T. C. program, and pilot training, its former students contributed heavily to the war effort. More than eighty former C. S. C. students died in the war. The College’s faculty also took part. Over one-third of the male teaching and research staff served in the armed forces or as advisers to the military. Several members of the faculty aided in weapons research, including work on the atom bomb. The College’s Extension Service and Experiment Station worked to maximize food production.
Fort Collins women took part in defense training classes which taught skills needed for war industries. Although excluded from foundry work, women were included in classes for welding, machine shop and sheet metal work.
To discover more about the decades and history of Fort Collins check out Fort Collins History Connection, the online collaboration between FCMoD and the Poudre River Public Library District: history.fcgov.com.