Post written by Alexa Leinaweaver, Live Animal Husbandry Coordinator.
The Pollinator You Know: The Honeybee!
When most people hear about pollination, the first thing they think of is the honeybee.
The oldest bee that scientists have found so far was in Myanmar, encased in amber and dated at 100 million years old! Bees that old were hunters, eating other insects. At some point they started visiting flowers for nectar and pollen, changing into the honeybees that we know and love.
Honeybee colonies have been kept in man-made hives since Ancient Egypt and have been important throughout human history. In addition to being delicious as a sweetener in food, honey can be used to make mead (an alcoholic drink), which works as an antiseptic. It has even been used to embalm mummies! Beeswax can be used in making many products, such as candles, soap, cosmetics, and waterproofing. Honey and bees are so important that people have named their children after bees. Deborah and Melissa both mean “bee” in different languages; Pamela derives from a word for “honey”.
When Europeans colonized the Americas in the 17th century, there were no native honeybees. Native Americans tribes at the time kept and traded other kinds of bees. European settlers brought the Western Honey Bee (Apis mellifera) along with their familiar crop plants when they moved to the Americas. As we have expanded across the planet, humans have deliberately expanded the range of the Western Honey Bee, and it is now found on every continent in the world except Antarctica.
Healthy Honeybee Colonies
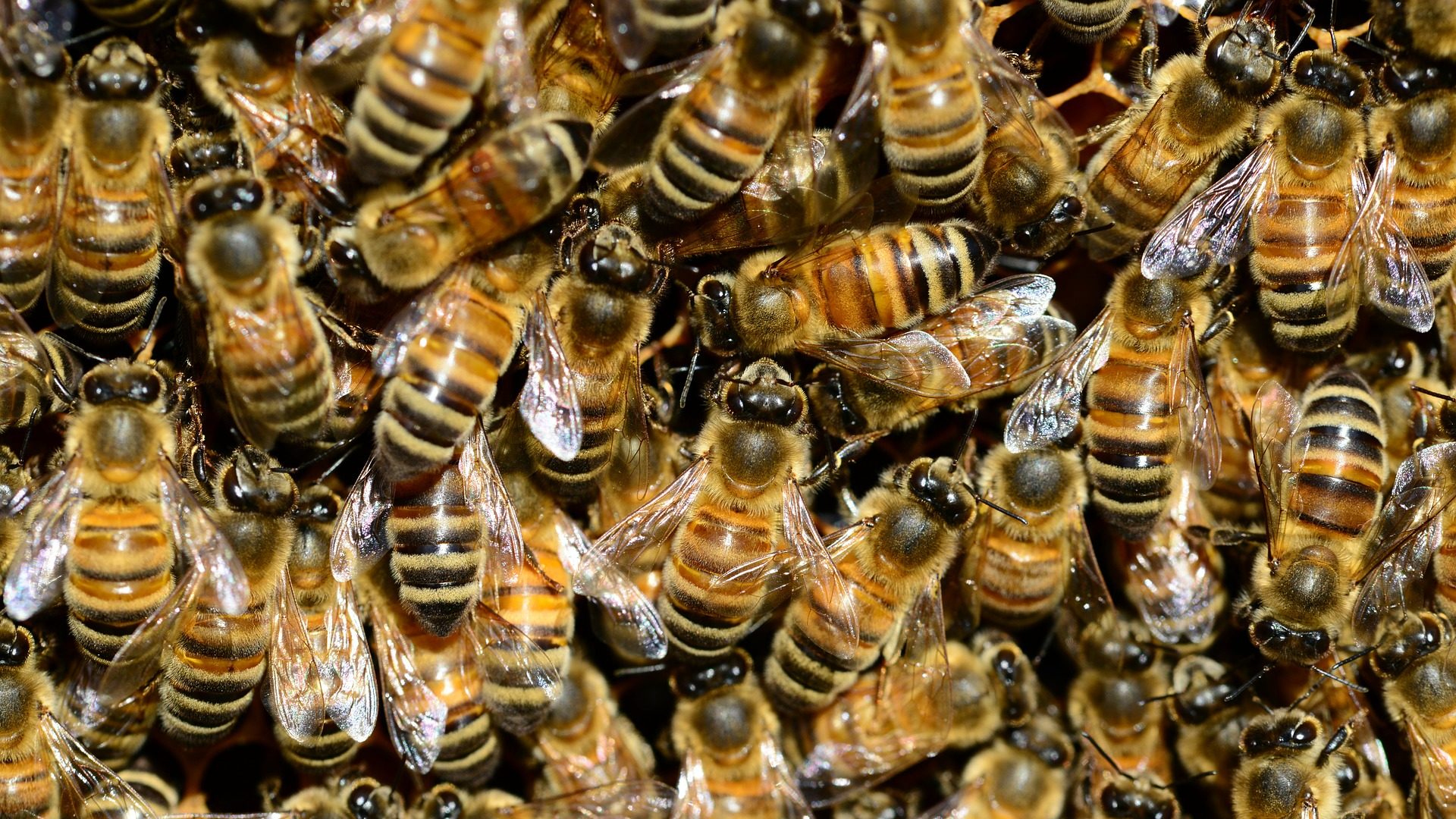
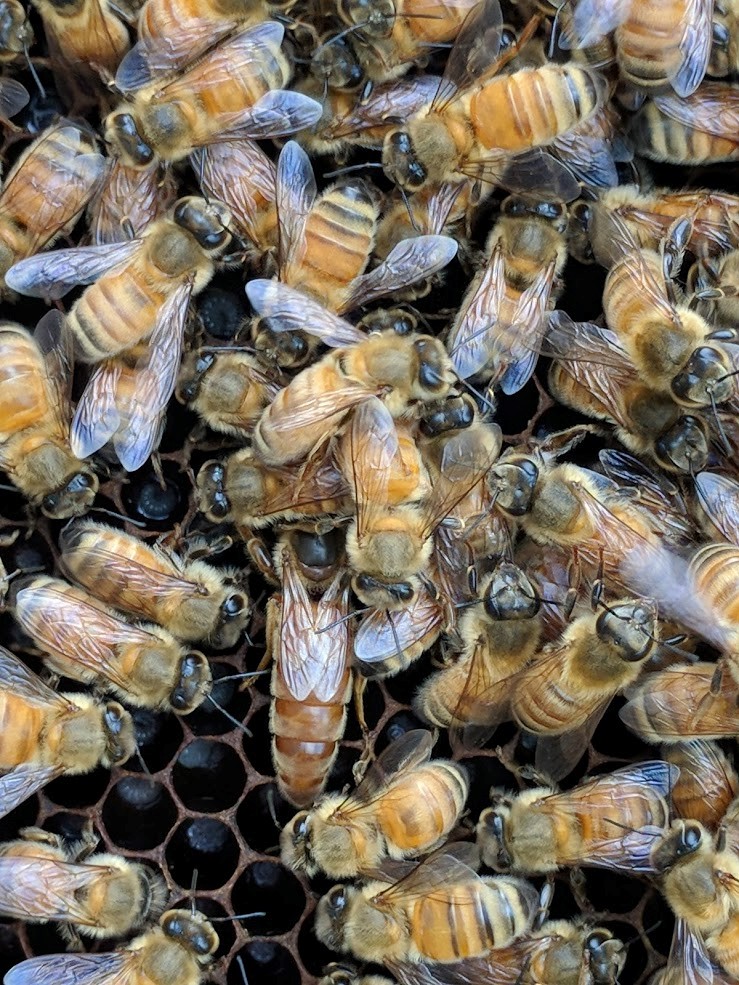
In a healthy honeybee colony, you can see thousands of individual bees. Most of what you see are the worker bees, which are females that cannot lay eggs. There are usually 10,000-50,000 workers per colony. The workers care for the queen and young, defend the hive with their stingers, build comb for the young honeybees and the honey, and collect food. There are also drones, which are the male honeybees. There are about 1,000 drones in a given colony. Drones have no sting, do not forage for food, and cannot defend the hive. Their only purpose is to mate with the queen. There is only one queen bee in the colony. She is larger than all the other bees, and usually has a circle of worker bees around her (her “court”) that take care of her, bringing her food and cleaning her. The queen is the only individual who can lay eggs, and can lay as many as 2,000 eggs per day!
The worker bees leave the hive and may fly up to two miles away from their home to find food. They seek out flowers and collect nectar, which is a sugary solution that flowers produce in order to attract pollinators. The worker bee then returns to the hive and performs a dance to indicate to her fellow workers where she found food. The collected nectar is transformed into honey and may be consumed by any of the adult bees or fed to the young who cannot yet fly to find their own food. The honey can also be harvested by humans.
Honeybee colonies normally survive for several years, going dormant in the winter cold and then becoming active in the warmer months. During favorable conditions (an abundance of food), the hive will create “daughter queens,” and the old queen and much of her colony will relocate to make room for the new queens.
What is happening with the FCMoD colony?
Fort Collins Museum of Discovery has had a bee colony in the Animal Encounters exhibit for our visitors to watch and enjoy since the exhibit opened. However, our colony has collapsed several times since then. Each time we have obtained a new colony from our professional beekeeper.
There are a lot of environmental factors that can negatively affect a honeybee colony, and a lot of colonies around the world are struggling and collapsing right now. There are some pesticides that are worse for bees, especially the class of pesticide called neonicotinoids. There are diseases and parasites that can affect a colony. Climate change may also be playing a factor with bee colonies dying.
What our beekeeper thinks may be happening to the honeybee colony here at FCMoD is that the bees may have found a flower source in the area that has been sprayed with a certain kind of pesticide. They collect the nectar and pesticide, then carry it back to the colony and tell their sisters where to find more. The bees eat the poisoned nectar and honey, and die.
How can we stop honeybee colony collapse?
There are a lot of different pesticides that people use to control weeds and to get rid of bugs they don’t like. But since we do like the honeybees and the honey they make, we need to make sure that we use pesticides that won’t hurt the bees. Pesticide application can be done at night when bees are not foraging. Additionally, making sure not to apply pesticides to blooming plants will help prevent bee deaths.
Like all animals, bees need good quality and abundant food. We can plant native flowers at our homes so honeybees and all the native Colorado bees have healthy and nutritious food sources.
We should also look for ways to reduce our impact on the environment around us, improving the lives of all animals that we share our environment with. Find reusable products instead of single use items you throw away. Turn off the lights in empty rooms. Compost. Take shorter showers. Each of us can have a huge positive impact on the wild animals that live around us.
Learn more about how pesticides can affect bees and other wildlife:
EPA Tips for Reducing Pesticide Impacts on Wildlife
National Pesticide Information Center: Protecting Wildlife from Pesticides
Learn about native plants you can use in your garden:
Colorado Native Plant Society plant lists
Find out how to reduce your impact on the environment:
World Wildlife Fund’s Tips for Reducing Your Environmental Impact
Can you spot the queen bee in this picture? She is larger and a slightly different color.

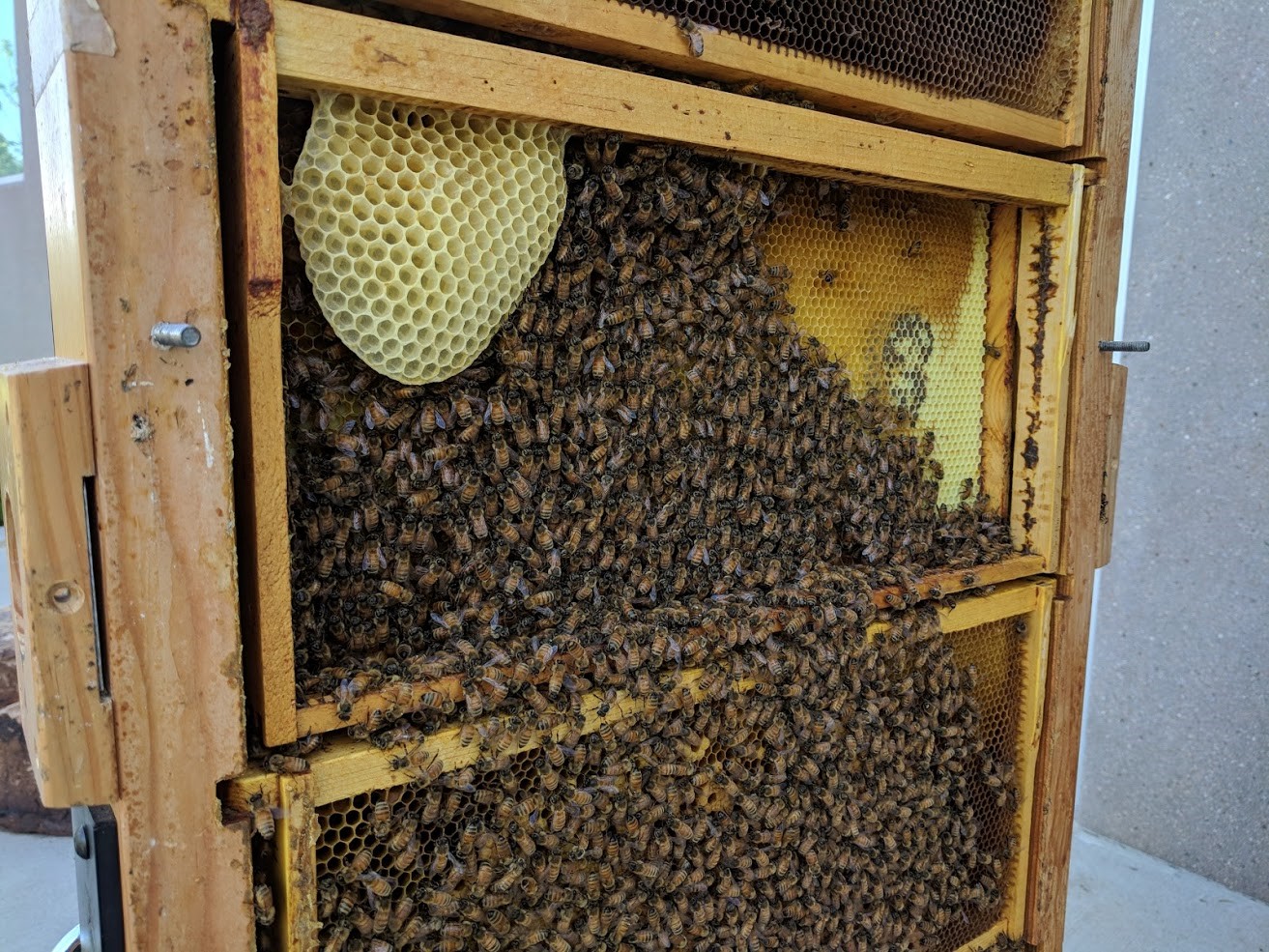
The FCMoD honeybee colony, in Spring of 2018.

Photos courtesy of Alexa Leinaweaver