Post written by Linda Moore, Curator of Collections
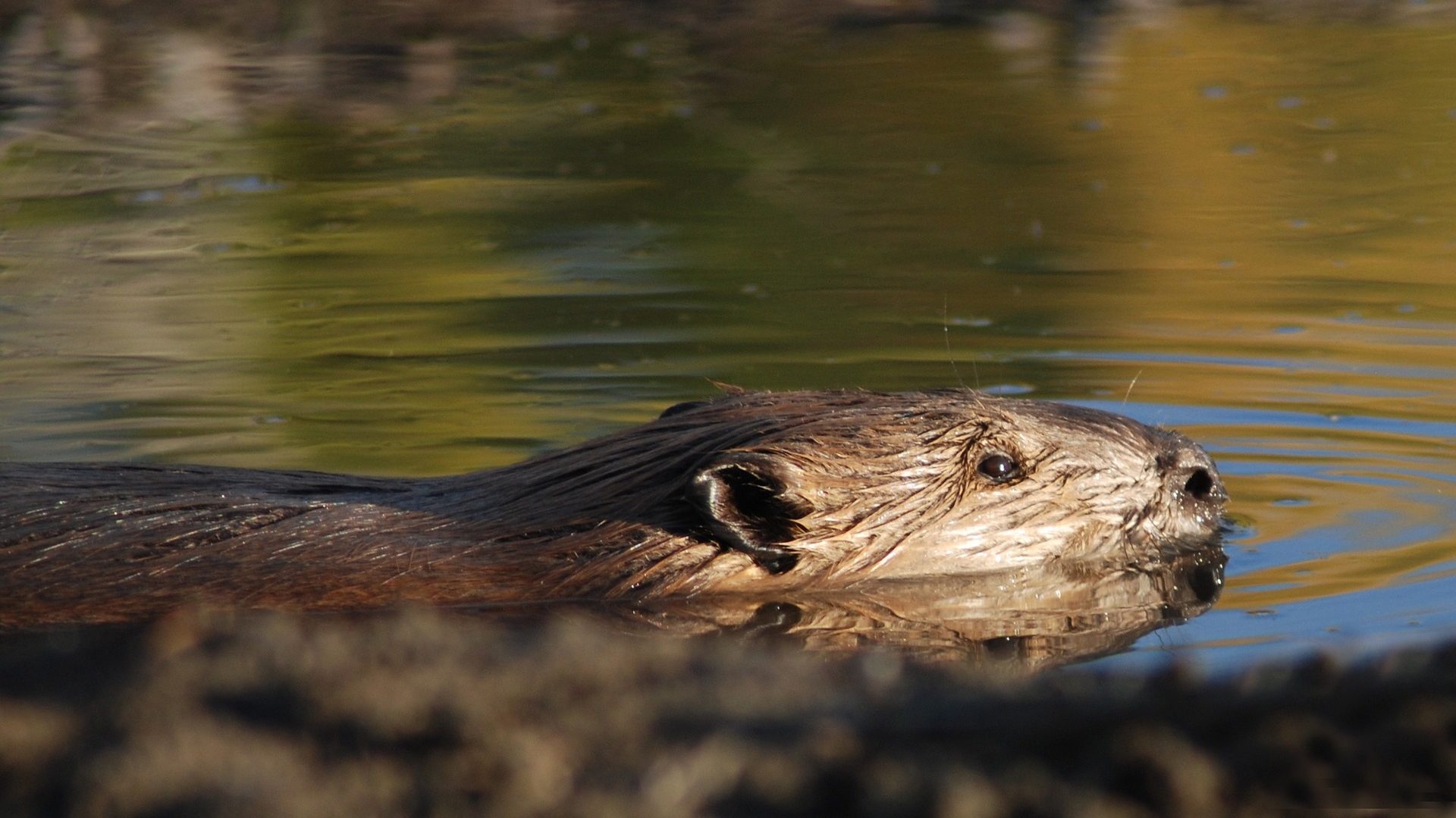
(A personal disclaimer: I grew up in Oregon–the Beaver State; in Corvallis, which is the home of Oregon State University and, of course, the mighty OSU Beavers. Our family drove around with twin stickers on our back-bumper declaiming “I’m a Beaver Believer” and “I’ve Got Beaver Fever.” I come by my love for these buck-toothed engineers honestly, and my “beaver fever” is unabashed.)
My experience with historical research has taught me that it can be almost impossible to pick up and follow a single topic: inevitably one thing is knotted on to another, tangled up with a dozen more, and sometimes tied on to its own tail. This has been the way it’s gone with my research on the beaver felt top hat of my last post. My research on that object made me curious to see what other artifacts of beaver history are preserved in the Fort Collins Museum of Discovery’s collections. Turns out it is an impressive inventory:
3 beaver felt top hats in addition to the one attributed to President Lincoln
1 elegant felt lady’s riding hat
2 wide-brimmed beaver felt Stetsons
1 pair of beaver fur mitts
1 bearskin coat trimmed at the collar and cuffs with beaver fur
1 sweet beaver fur cape and muff set, made from beavers trapped on George Campton’s ranch in Livermore about 1910 for his sister
1 old beaver trap, pulled out of the Cache La Poudre River and donated to the Museum in the 1960s
1 pelt from a beaver trapped by the donor himself in Colorado and donated in 1979
2 stuffed and mounted beavers (the largest and fattest dang beavers I’ve ever seen)
a set of beaver skulls
and, finally, various pairs of bright orange upper front beaver teeth
The presence of these beaver-related objects in the Museum’s collections reflects a steady involvement of the species in our region’s history, despite an economically driven “beaver fever” that severely depleted their numbers before Colorado had even become a state. The earliest historical trapping records of the Colorado Rocky Mountain region show sixty to eighty beaver present per mile of stream. By the turn of the 20th century the species’ population nationwide was as low as 100,000 individuals, very few of whom were here in the West.
Two sources I’ve come across recently not only decry the West’s loss of beaver populations, but advocate their protection and reintroduction as a means of conserving our region’s natural and cultural riches. Both recognize that in shaping the region’s waterways to their own purposes, beavers once played, and can play again, a vital role in maintaining the environments in which the region’s unique human history has unfolded. The first of these is Beaver World, a charming book by Enos Mills, a signed copy of which is in the Fort Collins Museum of Discovery’s Local History Archive. Mills was a passionate advocate for the natural world, and an astute direct observer of wild animals interacting with the environment. Beaver World was published in 1913, and in it Mills not only gushes about the beaver’s emblematic industriousness, “He works not only tooth and nail, but tooth and tail,” but more insightfully recognizes the role the species plays in maintaining both a healthy ecosystem, and a landscape humans find welcoming and pleasing:
Beaver works are of economical and educational value besides adding a charm to the wilds. The beaver is a persistent practicer of conservation and should not perish from the hills and mountains of our land. Altogether, the beaver has so many interesting ways, is so useful, skillful, practical, and picturesque that his life and his deeds deserve a larger place in literature and in our hearts.
The beaver’s role in maintaining healthy, functional Western ecosystems is the central focus in the much more contemporary article “Voyage of the Dammed,” carried in The High Country News. Writing at a time when water conservation is a high-profile problem and many of its proposed solutions carry high price tags, author Kevin Taylor outlines the position of environmentalists and other concerned citizens who advocate, at least in part, leaving it to the beavers:
The humble, hardworking rodent, through its dams and ponds, can extend the release of water late into summer, saturating the ground and healing watersheds. It has the power to re-create the primordial, wetter West that existed for millennia.
The article extends the beaver’s vital restorative role to cultural values as well. Taylor quotes a Coeur d’Alene tribal elder, 86-year-old Felix Aripa, who sees within the native ecosystems restored by beaver activity the roots of cultural restoration: in the returning native plants, fish, and animal species are embodied the cultural riches of language and long-held cultural knowledge.
These two sources have whetted my appetite for learning more about this species, and for doing what I can to promote its ongoing presence in our region. I understand that in caring for the beaver artifacts which lie within the Fort Collins Museum of Discovery’s collection — clothing, tools, and scientific specimens — we preserve the history of a species which plays a central role in the Native American traditions of this area, as well as in the story of the region’s surge in population and development in the 19th century. As I read the strong praise Enos Mills gives this species and the excited plans of those advocating its restoration, I’m thrilled with the possibility that within today’s beaver population is preserved a solution to our region’s compelling need to conserve both the health of the environment and the wealth of our cultural and historical heritage. “I’m a Beaver Believer” indeed.
Continue Reading